Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer in brief:
Explain what is the optical path length. How is it different from actual path length?
What is Optical Path length? How is it different from the actual Path length?
उत्तर १
Consider, a light wave with an angular frequency of w and a wave vector of k travelling in the x-direction through a vacuum. The phase of this wave is (kx - ωt). In a vacuum, light speed at c, but in a medium, it speeds at v.
k = `(2pi)/lambda = (2pi v)/(v lambda) = omega/v` as ω = 2πv and v = vλ, where v is the frequency of light.
If the wave travels a distance Δ x, its phase changes by Δ Φ = kΔx = ω Δx/v.
Similarly, if the wave is travelling in vacuum,
k = ω/c and Δ Φ = ω Δ x/c
Now, consider a wave travelling a distance Δ x in the medium, the phase difference generated is,
Δ Φ' = k' Δ x = ωn Δ x/c = ω Δ x'/c ...(1)
where Δ x' = n Δ x .....(2)
The distance nΔ x is called the optical path length of the light in the medium; it is the distance the light would have travelled in the same time t in vacuum (with the speed c).
The optical path length in a medium is the corresponding path in a vacuum that light traverses at the same time as it does in the medium.
Now, speed = `"distance"/"time"`
∴ time = `"distance"/"speed"`
∴ t = `"d"_"medium"/"v"_"medium" = "d"_"vaccum"/"v"_"vaccum"`
Hence, the optical path = `"d"_"vacuum"`
`= "v"_"vaccum"/"v"_"medium" xx "d"_"medium"`
`= "n" xx "d"_"medium"`
Thus, a distance d travelled in a medium of refractive index n introduces a path difference = nd - d = d (n - 1) over a ray travelling equal distance through vacuum.
उत्तर २
i. When a wave travels a distance Δx through a medium having a refractive index of n, its phase changes by the same amount as it would if the wave had travelled a distance nΔx in a vacuum.
ii. Thus, a path length of Δx in a medium of refractive index n is equivalent to a path length of nΔx in a vacuum.
iii. nΔx is called the optical path travelled by a wave.
iv. This means, the optical path through a medium is the effective path travelled by light in a vacuum to generate the same phase difference.
v. Optical path in a medium can also be defined as the corresponding path in a vacuum that the light travels at the same time as it takes in the given medium.
i.e., time = `"d"_"medium"/"v"_"medium" = "d"_"vacuum"/"v"_"vacuum"`
∴ `"d"_"vacuum" = "v"_"vacuum"/"v"_"medium" xx "d"_"medium" = "n" xx "d"_"medium"`
But `"d"_"vacuum"` = Optical path
∴ Optical path = n × `"d"_"medium"`
Thus, a distance d travelled in a medium of refractive index n introduces a path difference = nd - d = d(n - 1) over a ray travelling an equal distance through the vacuum.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Laser light of wavelength 630 nm is incident on a pair of slits which are separated by 1.8 mm. If the screen is kept 80 cm away from the two slits, calculate:
1) fringe separation i.e. fringe width.
2) distance of 10th bright fringe from the centre of the interference pattern
A long narrow horizontal slit is paced 1 mm above a horizontal plane mirror. The interference between the light coming directly from the slit and that after reflection is seen on a screen 1.0 m away from the slit. Find the fringe-width if the light used has a wavelength of 700 nm.
Answer the following question.
Describe any two characteristic features which distinguish between interference and diffraction phenomena. Derive the expression for the intensity at a point of the interference pattern in Young's double-slit experiment.
Answer in brief:
In Young's double-slit experiment what will we observe on the screen when white light is incident on the slits but one slit is covered with a red filter and the other with a violet filter? Give reasons for your answer.
Draw a neat labelled ray diagram of the Fresnel Biprism experiment showing the region of interference.
Obtain the relation between phase difference and path difference.
Obtain the equation for resultant intensity due to interference of light.
Obtain the equation for bandwidth in Young’s double slit experiment.
Discuss the interference in thin films and obtain the equations for constructive and destructive interference for transmitted and reflected light.
Light of wavelength 600 nm that falls on a pair of slits producing interference pattern on a screen in which the bright fringes are separated by 7.2 mm. What must be the wavelength of another light which produces bright fringes separated by 8.1 mm with the same apparatus?
The interference pattern is obtained with two coherent light sources of intensity ratio n. In the interference pattern, the ratio `("I"_"max" - "I"_"min")/("I"_"max" + "I"_"min")` will be ______
In Young's double slit experiment green light is incident on the two slits. The interference pattern is observed on a screen. Which one of the following changes would cause the observed fringes to be more closely spaced?
A metal rod has length, cross-sectional area and Young's modulus as L, A and Y, respectively. If the elongation in the rod produced is l, then work done is proportional to ______.
A thin transparent sheet is placed in front of a slit in Young's double slit experiment. The fringe width will ____________.
Band width for red light of wavelength 6600 Å is 0.42 mm. If red Light is replaced by blue light of wavelength 4400 Å, then the change m bandwidth will be ____________.
In Young's experiment, the distance between the slits is doubled and the distance between the slit and screen is reduced to half, then the fringe width ____________.
In a double slit experiment, the two slits are 2 mm apart and the screen is placed 1 m away. A monochromatic light of wavelength 500 nm is used. What will be the width of each slit for obtaining ten maxima of double slit within the central maxima of single slit pattern?
In Young's double-slit experiment, an interference pattern is obtained on a screen by a light of wavelength 4000 Å, coming from the coherent sources S1 and S2 At certain point P on the screen, third dark fringe is formed. Then the path difference S1P - S2P in microns is ______.
Two sources of light 0.5 mm apart are placed at a distance of 2.4 m and wavelength of light is 5000 Å. The phase difference between the two light waves interfering on the screen at a point at a distance 3 mm from central bright band is ____________.
In the biprism experiment, a source of monochromatic light is used for a certain distance between slit and eyepiece. When the distance between two virtual sources is changed from dA to dB, then the fringe width is changed from ZA to ZB. The ratio ZA to ZB is ______
In Young's double-slit experiment, the distance between the slits is 3 mm and the slits are 2 m away from the screen. Two interference patterns can be obtained on the screen due to light of wavelength 480 nm and 600 run respectively. The separation on the screen between the 5th order bright fringes on the two interference patterns is ______
In an interference experiment, the intensity at a point is `(1/4)^"th"` of the maximum intensity. The angular position of this point is at ____________.
(cos 60° = 0.5, `lambda` = wavelength of light, d = slit width)
Two coherent sources of intensities I1 and I2 produce an interference pattern on the screen. The maximum intensity in the interference pattern is ______
If we have two coherent sources S1 and S2 vibrating in phase, then for an arbitrary point P constructive interference is observed whenever the path difference is ______.
What is meant by Constructive interference?
The path difference between two interference light waves meeting at a point on the screen is `(87/2)lambda`. The band obtained at that point is ______.
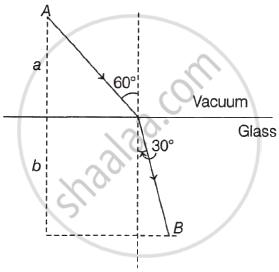
A ray of light AO in vacuum is incident on a glass slab at angle 60° and refracted at angle 30° along OB as shown in the figure. The optical path length of light ray from A to B is ______.