Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Discuss the interference in thin films and obtain the equations for constructive and destructive interference for transmitted and reflected light.
उत्तर
- Interference in thin films:
- Let us consider a thin film of transparent material of refractive index p (not to confuse with an order of fringe n) and thickness d. A parallel beam of light is incident on the film at an angle i.
- The wave is divided into two parts at the upper surface, one is reflected and the other is refracted. The refracted part, which enters into the film, again gets divided at the lower surface into two parts; one is transmitted out of the film and the other is reflected back into the film.
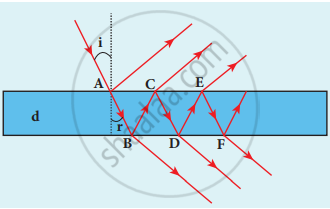
Interference in thin films
- For transmitted light:
- The light transmitted may interfere to produce a resultant intensity. Let us consider the path difference between the two light waves transmitted from B and D. The two waves moved together and remained in phase up to B where splitting occurred.
- The extra path travelled by the wave transmitted from D is the path inside the film, BC + CD. If we approximate the incidence to be nearly normal (i = 0), then points B and D are very close to each other. The extra distance travelled by the wave is approximately twice thickness of the film, BC + CD = 2d. As this extra path is travelled in a medium of refractive index p, the optical path difference is,
δ = 2μd. - The condition for constructive interference in transmitted ray is,
2μd = nλ
Similarly, the condition for destructive interference in transmitted ray is
2μd = (2n-l) `λ/2`
- For reflected light:
- Wave while travelling in a rarer medium and getting reflected by a denser medium, undergoes a phase change of n or an additional path difference of `λ/2`.
- Let us consider the path difference between the light waves reflected by the upper surface at A and the other wave coming out at C after passing through the film.
- The additional path travelled by wave coming out from C is the path inside the film, AB + BC. For nearly normal incidence this distance could be approximated as, AB + BC = 2d. As this extra path is travelled in the medium of refractive index p, the optical path difference is, δ = 2μd.
- The condition for constructive interference for reflected ray is,
2μd + `λ/2` = nλ (or)
2μd = (2n – 1) `λ/2` - The additional path difference λ/2 is due to the phase change of n in rarer to denser reflection taking place at A. The condition for destructive interference for a reflected ray is,
2μd + `λ/2` = (2n + l)`λ/2` (or)
2μd = nλ
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Laser light of wavelength 630 nm is incident on a pair of slits which are separated by 1.8 mm. If the screen is kept 80 cm away from the two slits, calculate:
1) fringe separation i.e. fringe width.
2) distance of 10th bright fringe from the centre of the interference pattern
A narrow slit S transmitting light of wavelength λ is placed a distance d above a large plane mirror, as shown in the following figure. The light coming directly from the slit and that coming after the reflection interfere at a screen ∑ placed at a distance D from the slit. (a) What will be the intensity at a point just above the mirror, i.e. just above O? (b) At what distance from O does the first maximum occur?
A long narrow horizontal slit is paced 1 mm above a horizontal plane mirror. The interference between the light coming directly from the slit and that after reflection is seen on a screen 1.0 m away from the slit. Find the fringe-width if the light used has a wavelength of 700 nm.
Describe geometry of the Young’s double slit experiment with the help of a ray diagram. What is fringe width? Obtain an expression of it. Write the conditions for constructive as well as destructive interference.
What is intensity (or) amplitude division?
What is a bandwidth of interference pattern?
Explain Young’s double-slit experimental setup and obtain the equation for path difference.
Obtain the equation for bandwidth in Young’s double slit experiment.
The interference pattern is obtained with two coherent light sources of intensity ratio n. In the interference pattern, the ratio `("I"_"max" - "I"_"min")/("I"_"max" + "I"_"min")` will be ______
A thin transparent sheet is placed in front of a slit in Young's double slit experiment. The fringe width will ____________.
The light waves from two independent monochromatic light sources are given by, y1 = 2 sin ωt and y2 = 3 cos ωt. Then the correct statement is ____________.
Band width for red light of wavelength 6600 Å is 0.42 mm. If red Light is replaced by blue light of wavelength 4400 Å, then the change m bandwidth will be ____________.
A thin mica sheet of thickness 4 x 10-6 m and refractive index 1.5 is introduced in the path of the first wave. The wavelength of the wave used is 5000 A. The central bright maximum will shift ______.
In Young's double slit experiment, the two slits act as coherent sources of equal amplitude A and wavelength `lambda`. In another experiment with the same set up the two slits are of equal amplitude A and wavelength `lambda`. but are incoherent. The ratio of the intensity of light at the mid-point of the screen in the first case to that in the second case is ____________.
`phi "and" phi_2 (phi_1 > phi_2)` are the work functions of metals A and B. When light of same wavelength is incident on A and B, the fastest emitted electrons from A are ____________ those emitted from B.
In the biprism experiment, the fringe width is 0.4 mm. What is the distance between the 4th dark band and the 6th bright band on the same side?
Show graphically the intensity distribution in a single slit diffraction pattern.
Two coherent sources P and Q produce interference at point A on the screen where there is a dark band which is formed between 4th bright band and 5th bright band. Wavelength of light used is 6000 Å. The path difference between PA and QA is ______.
The path difference between two interference light waves meeting at a point on the screen is `(87/2)lambda`. The band obtained at that point is ______.
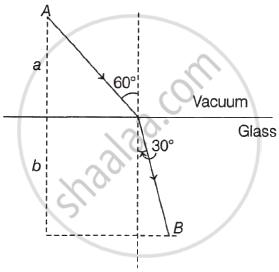
A ray of light AO in vacuum is incident on a glass slab at angle 60° and refracted at angle 30° along OB as shown in the figure. The optical path length of light ray from A to B is ______.