Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Apart from tetrahedral geometry, another possible geometry for CH4 is square planar with the four H atoms at the corners of the square and the C atom at its centre. Explain why CH4 is not square planar?
उत्तर १
According to VSEPR theory, if CH4 were square planar, the bond angle would be 90°. For tetrahedral structure, the bond angle is 109°28′. Therefore, in square planar structure, repulsion between bond pairs would be more and thus the stability will be less.
उत्तर २
Electronic configuration of carbon atom:
6C: 1s2 2s2 2p2
In the excited state, the orbital picture of carbon can be represented as:
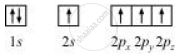
Hence, carbon atom undergoes sp3 hybridization in CH4 molecule and takes a tetrahedral shape.
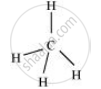
For a square planar shape, the hybridization of the central atom has to be dsp2. However, an atom of carbon does not have d-orbitalsto undergo dsp2 hybridization. Hence, the structure of CH4 cannot be square planar.
Moreover, with a bond angle of 90° in square planar, the stability of CH4 will be very less because of the repulsion existing between the bond pairs. Hence, VSEPR theory also supports a tetrahedral structure for CH4.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a diagram showing the formation of a double bond and a triple bond between carbon atoms in C2H4 and C2H2 molecules.
What is the total number of sigma and pi bonds in the following molecules?
C2H2
Distinguish between a sigma and a pi bond.
What is the total number of sigma and pi bonds in the following molecules?
C2H4
The types of hybrid orbitals of nitrogen in \[\ce{NO^{+}2}\] , \[\ce{NO^{-}3}\] and \[\ce{NH^{+}4}\] respectively are expected to be ______.
Predict the shapes of the following molecules on the basis of hybridisation.
\[\ce{BCl3, CH4 , CO2, NH3}\]
Match the shape of molecules in Column I with the type of hybridisation in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Tetrahedral | (a) sp2 |
| (ii) Trigonal | (b) sp |
| (iii) Linear | (c) sp3 |
Discuss the concept of hybridisation. What are its different types in a carbon atom.
What is the type of hybridisation of carbon atoms marked with star.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.....}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{.....}||\\
\ce{\overset{∗}{C}H2 = CH - \overset{∗}{C} - O - H}
\end{array}\]
What is the type of hybridisation of carbon atoms marked with star.
\[\ce{\overset{∗}{C}H3 - CH = CH - CH3}\]
What is the type of hybridisation of carbon atoms marked with star.
\[\ce{CH3 - \overset{∗}{C} ≡ CH}\]
In the given reaction,
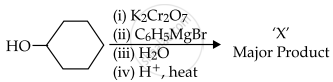
the number of sp2 hybridised carbon (s) in compound 'X' is ______.
In which of the following species S atom assumes sp3 hybrid state?
(I) (SO3)
(II) SO2
(III) H2S
(IV) S8
The hybridisation of carbanion is:
