Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Apart from tetrahedral geometry, another possible geometry for CH4 is square planar with the four H atoms at the corners of the square and the C atom at its centre. Explain why CH4 is not square planar?
उत्तर १
According to VSEPR theory, if CH4 were square planar, the bond angle would be 90°. For tetrahedral structure, the bond angle is 109°28′. Therefore, in square planar structure, repulsion between bond pairs would be more and thus the stability will be less.
उत्तर २
Electronic configuration of carbon atom:
6C: 1s2 2s2 2p2
In the excited state, the orbital picture of carbon can be represented as:
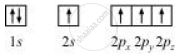
Hence, carbon atom undergoes sp3 hybridization in CH4 molecule and takes a tetrahedral shape.
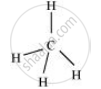
For a square planar shape, the hybridization of the central atom has to be dsp2. However, an atom of carbon does not have d-orbitalsto undergo dsp2 hybridization. Hence, the structure of CH4 cannot be square planar.
Moreover, with a bond angle of 90° in square planar, the stability of CH4 will be very less because of the repulsion existing between the bond pairs. Hence, VSEPR theory also supports a tetrahedral structure for CH4.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What do you understand by bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons? Illustrate by giving one example of each type.
What is the total number of sigma and pi bonds in the following molecules?
C2H4
Isostructural species are those which have the same shape and hybridisation. Among the given species identify the isostructural pairs.
The types of hybrid orbitals of nitrogen in \[\ce{NO^{+}2}\] , \[\ce{NO^{-}3}\] and \[\ce{NH^{+}4}\] respectively are expected to be ______.
Which of the following angle corresponds to sp2 hybridisation?
Predict the shapes of the following molecules on the basis of hybridisation.
\[\ce{BCl3, CH4 , CO2, NH3}\]
Match the species in Column I with the type of hybrid orbitals in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) \[\ce{SF4}\] | (a) sp3d2 |
| (ii) \[\ce{IF5}\] | (b) d2sp3 |
| (iii) \[\ce{NO^{+}2}\], | (c) sp3d |
| (iv) \[\ce{NH^{+}4}\], | (d) sp3 |
| (e) sp |
Match the shape of molecules in Column I with the type of hybridisation in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Tetrahedral | (a) sp2 |
| (ii) Trigonal | (b) sp |
| (iii) Linear | (c) sp3 |
Discuss the concept of hybridisation. What are its different types in a carbon atom.
What is the type of hybridisation of carbon atoms marked with star.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.....}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{.....}||\\
\ce{\overset{∗}{C}H2 = CH - \overset{∗}{C} - O - H}
\end{array}\]
What is the type of hybridisation of carbon atoms marked with star.
\[\ce{CH3 - \overset{∗}{C}H2 - OH}\]
What is the type of hybridisation of carbon atoms marked with star.
\[\ce{CH3 - \overset{∗}{C} ≡ CH}\]
BF3 is a planar and electron-deficient compound. Hybridization and the number of electrons around the central atom, respectively are ______.
In which of the following species S atom assumes sp3 hybrid state?
(I) (SO3)
(II) SO2
(III) H2S
(IV) S8
