Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Balance the following reaction by oxidation number method.
\[\ce{MnO^-_{4(aq)} + Br^-_{ (aq)}->MnO2_{ (s)} + BrO^-_{3(aq)}(basic)}\]
उत्तर
\[\ce{MnO^-_{4(aq)} + Br^-_{ (aq)}->MnO2_{ (s)} + BrO^-_{3(aq)}(basic)}\]
Step 1: Write a skeletal equation and balance the elements other than O and H.
\[\ce{MnO^-_{4(aq)} + Br^-_{ (aq)}->MnO2_{ (s)} + BrO^-_{3(aq)}}\]
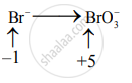
Step 2: Assign the oxidation number to Mn and Br. Calculate the increase and decrease in the oxidation number and make them equal.
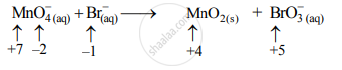
Increase in oxidation number:
(Increase per atom = 6)
Decrease in oxidation number:
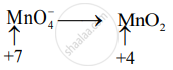
(Decrease per atom = 3)
To make the net increase and decrease equal, we must take 2 atoms of Mn.
\[\ce{2MnO^-_{4(aq)} + Br^-_{ (aq)}->2MnO2_{ (s)} + BrO^-_{3(aq)}}\]
Step 3: Balance 'O' atoms by adding H2O to the right-hand side.
\[\ce{2MnO^-_{4(aq)} + Br^-_{ (aq)}->2MnO2_{ (s)} + BrO^-_{3(aq)} + H2O_{(l)}}\]
Step 4: The medium is basic. To make the charges and hydrogen atoms on the two sides equal, add 2H+ on the left-hand side.
\[\ce{2MnO^-_{4(aq)} + Br^-_{ (aq)} + 2H^+_{ (aq)}->2MnO2_{ (s)} + BrO^-_{3(aq)} + H2O_{(l)}}\]
Add OH− ions equal to the number of H+ ions on both sides of the equation.
\[\ce{2MnO^-_{4(aq)} + Br^-_{ (aq)} + 2H^+_{ (aq)} + 2OH^-_{( aq)}->2MnO2_{ (s)} + BrO^-_{3(aq)} + H2O_{(l)} + 2OH^-_{( aq)}}\]
The H+ and OH− ions appearing on the same side of the reaction are combined to give H2O molecules.
\[\ce{2MnO^-_{4(aq)} + Br^-_{ (aq)} + 2H2O_{(l)}->2MnO2_{ (s)} + BrO^-_{3(aq)} + H2O_{(l)} + 2OH^-_{( aq)}}\]
\[\ce{2MnO^-_{4(aq)} + Br^-_{ (aq)} + H2O_{(l)}->2MnO2_{ (s)} + BrO^-_{3(aq)} + 2OH^-_{( aq)}}\]
Step 5: Check two sides for balance of atoms and charges.
Hence, balanced equation: \[\ce{2MnO^-_{4(aq)} + Br^-_{ (aq)} + H2O_{(l)}->2MnO2_{ (s)} + BrO^-_{3(aq)} + 2OH^-_{( aq)}}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Calculate the oxidation number of sulphur, chromium and nitrogen in H2SO5, `"Cr"_2"O"_7^(2-)` and `"NO"_3^-`. Suggest structure of these compounds. Count for the fallacy.
Whenever a reaction between an oxidising agent and a reducing agent is carried out, a compound of lower oxidation state is formed if the reducing agent is in excess and a compound of higher oxidation state is formed if the oxidising agent is in excess. Justify this statement giving three illustrations.
Balance the following redox reactions by ion-electron method:
- \[\ce{MnO-_4 (aq) + I– (aq) → MnO2 (s) + I2(s) (in basic medium)}\]
- \[\ce{MnO-_4 (aq) + SO2 (g) → Mn^{2+} (aq) + HSO-_4 (aq) (in acidic solution)}\]
- \[\ce{H2O2 (aq) + Fe^{2+} (aq) → Fe^{3+} (aq) + H2O (l) (in acidic solution)}\]
- \[\ce{Cr_2O^{2-}_7 + SO2(g) → Cr^{3+} (aq) + SO^{2-}_4 (aq) (in acidic solution)}\]
Balance the following equation in basic medium by ion-electron method and oxidation number methods and identify the oxidising agent and the reducing agent.
\[\ce{Cl_2O_{7(g)} + H_2O_{2(aq)} -> ClO-_{2(aq)} + O_{2(g)} + H+_{(aq)}}\]
The Mn3+ ion is unstable in solution and undergoes disproportionation to give Mn2+, MnO2, and H+ ion. Write a balanced ionic equation for the reaction.
Justify that the following reaction is redox reaction; identify the species oxidized/reduced, which acts as an oxidant and which acts as a reductant.
\[\ce{2Cu2O_{(S)} + Cu2S_{(S)}->6Cu_{(S)} + SO2_{(g)}}\]
Balance the following reaction by oxidation number method.
\[\ce{H2SO4_{(aq)} + C_{(s)}->CO2_{(g)} + SO2_{(g)} + H2O_{(l)}(acidic)}\]
Identify coefficients 'x' and 'y' for the following reaction.
\[\ce{{x}H2O2_{(aq)} + ClO^-_{4(aq)} -> 2O2_{(g)} + ClO^-_{2(aq)} + {y}H2O_{(l)}}\]
Which of the following is a redox reaction?
What is the change in oxidation number of Sulphur in following reaction?
\[\ce{MnO^-_{4(aq)} + SO^{2-}_{3(aq)} -> MnO^{2-}_{4(aq)} + SO^{2-}_{4(aq)}}\]
Consider the reaction:
\[\ce{6 CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) → C6 H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g)}\]
Why it is more appropriate to write these reaction as:
\[\ce{6CO2(g) + 12H2O(l) → C6 H12O6(aq) + 6H2O(l) + 6O2(g)}\]
Also, suggest a technique to investigate the path of the redox reactions.
Write balanced chemical equation for the following reactions:
Reaction of liquid hydrazine \[\ce{(N2H4)}\] with chlorate ion \[\ce{(ClO^{-}3)}\] in basic medium produces nitric oxide gas and chloride ion in gaseous state.
Balance the following equations by the oxidation number method.
\[\ce{Fe^{2+} + H^{+} + Cr2O^{2-}7 -> Cr^{3+} + Fe^{3+} + H2O}\]
Balance the following equations by the oxidation number method.
\[\ce{I2 + NO^{-}3 -> NO2 + IO^{-}3}\]
Balance the following equations by the oxidation number method.
\[\ce{I2 + S2O^{2-}3 -> I- + S4O^{2-}6}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{3HCl (aq) + HNO3 (aq) -> Cl2 (g) + NOCl (g) + 2H2O (l)}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{HgCl2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) -> HgI2 (s) + 2KCl (aq)}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{4NH3 (g) + 3O2 (g) -> 2N2 (g) + 6H2O (g)}\]
Balance the following ionic equations.
\[\ce{Cr2O^{2-}7 + H^{+} + I- -> Cr^{3+} + I2 + H2O}\]
Balance the following ionic equations.
\[\ce{Cr2O^{2-}7 + Fe^{2+} + H+ -> Cr^{3+} + Fe^{3+} + H2O}\]
Balance the following ionic equations.
\[\ce{MnO^{-}4 + H^{+} + Br^{-} -> Mn^{2+} + Br2 + H2O}\]
In acidic medium, reaction, \[\ce{MNO^-_4 → Mn^2+}\] an example of ____________.
\[\ce{H2O2 -> 2H^+ + O2 + 2e^-}\]; E0 = −0.68 V.
This equation represents which of the following behaviour of H2O2?
