Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Balance the following redox equation by half-reaction method.
\[\ce{H2C2O_{4(aq)} + MnO^-_{4(aq)}->CO2_{(g)} + Mn^2+_{( aq)}(acidic)}\]
उत्तर
\[\ce{H2C2O_{4(aq)} + MnO^-_{4(aq)}->CO2_{(g)} + Mn^2+_{( aq)}}\]
Step 1: Write the unbalanced equation for the redox reaction. Assign the oxidation number to all the atoms in reactants and products. Divide the equation into two half equations.
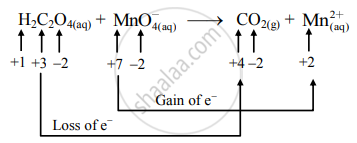
- Oxidation half-reaction: \[\ce{H2C2O_{4(aq)}->CO2_{(g)}}\]
- Reduction half-reaction: \[\ce{MnO^-_{4(aq)}->Mn^2+_{( aq)}}\]
Step 2: Balance the atoms except O and H in each half equation. Balance half equation for O atoms by adding 4H2O to the right side of the reduction half equation.
- Oxidation: \[\ce{H2C2O_{4(aq)}->2CO2_{(g)}}\]
- Reduction: \[\ce{MnO^-_{4(aq)}->Mn^2+_{( aq)} + 4H2O_{(l)}}\]
Step 3: Balance H atoms by adding H+ ions to the side with less H. Hence, add 2H+ ions to the right side of the oxidation half equation and 8H+ ions to the left side of the reduction half equation.
- Oxidation: \[\ce{H2C2O_{4(aq)}->2CO2_{(g)} + 2H^+_{( aq)}}\]
- Reduction: \[\ce{MnO^-_{4(aq)} + 8H^+_{( aq)}->Mn^2+_{( aq)} + 4H2O_{(l)}}\]
Step 4: Now add 2 electrons to the right side of the oxidation half equation and 5 electrons to the left side of the reduction half equation to balance the charges.
- Oxidation: \[\ce{H2C2O_{4(aq)}->2CO2_{(g)} + 2H^+_{( aq)} + 2e^-}\]
- Reduction: \[\ce{MnO^-_{4(aq)} + 8H^+_{( aq)} + 5e^-->Mn^2+_{( aq)} + 4H2O_{(l)}}\]
Step 5: Multiply oxidation half equation by 5 and reduction half equation by 2 to equalize the number of electrons in two half equations. Then add two half equations.
- Oxidation: \[\ce{5H2C2O_{4(aq)}->10CO2_{(g)} + 10H^+_{( aq)} + 10e^-}\]
- Reduction: \[\ce{2MnO^-_{4(aq)} + 16H^+_{( aq)} + 10e^-->2Mn^2+_{( aq)} + 8H2O_{(l)}}\]
Add two half equations:
\[\ce{5H2C2O_{4(aq)} + 2MnO^-_{4(aq)} + 6H^+_{( aq)}->10CO2 + 2Mn^2+_{( aq)} + 8H2O_{(l)}}\]
The equation is balanced in terms of the number of atoms and the charges.
Hence, balanced equation: \[\ce{5H2C2O_{4(aq)} + 2MnO^-_{4(aq)} + 6H^+_{( aq)}->10CO2 + 2Mn^2+_{( aq)} + 8H2O_{(l)}}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Balance the following redox reactions by ion-electron method:
- \[\ce{MnO-_4 (aq) + I– (aq) → MnO2 (s) + I2(s) (in basic medium)}\]
- \[\ce{MnO-_4 (aq) + SO2 (g) → Mn^{2+} (aq) + HSO-_4 (aq) (in acidic solution)}\]
- \[\ce{H2O2 (aq) + Fe^{2+} (aq) → Fe^{3+} (aq) + H2O (l) (in acidic solution)}\]
- \[\ce{Cr_2O^{2-}_7 + SO2(g) → Cr^{3+} (aq) + SO^{2-}_4 (aq) (in acidic solution)}\]
Balance the following equation in basic medium by ion-electron method and oxidation number methods and identify the oxidising agent and the reducing agent.
\[\ce{P4(s) + OH–(aq) —> PH3(g) + HPO^–_2(aq)}\]
Balance the following equation in the basic medium by ion-electron method and oxidation number methods and identify the oxidising agent and the reducing agent.
\[\ce{N2H4(l) + ClO^-_3 (aq) → NO(g) + Cl–(g)}\]
Balance the following equation in basic medium by ion-electron method and oxidation number methods and identify the oxidising agent and the reducing agent.
\[\ce{Cl_2O_{7(g)} + H_2O_{2(aq)} -> ClO-_{2(aq)} + O_{2(g)} + H+_{(aq)}}\]
The Mn3+ ion is unstable in solution and undergoes disproportionation to give Mn2+, MnO2, and H+ ion. Write a balanced ionic equation for the reaction.
In Ostwald’s process for the manufacture of nitric acid, the first step involves the oxidation of ammonia gas by oxygen gas to give nitric oxide gas and steam. What is the maximum weight of nitric oxide that can be obtained starting only with 10.00 g. of ammonia and 20.00 g of oxygen?
Choose the correct option.
For the following redox reactions, find the correct statement.
\[\ce{Sn^{2⊕} + 2Fe^{3⊕}->Sn^{4⊕} + 2Fe^{2⊕}}\]
Balance the following reaction by oxidation number method.
\[\ce{H2SO4_{(aq)} + C_{(s)}->CO2_{(g)} + SO2_{(g)} + H2O_{(l)}(acidic)}\]
Balance the following reaction by oxidation number method.
\[\ce{Bi(OH)_{3(s)} + Sn(OH)^-_{3(aq)}->Bi_{(s)} + Sn(OH)^2-_{6(aq)}(basic)}\]
Balance the following redox equation by half-reaction method.
\[\ce{Bi(OH)_{3(s)} + SnO^2-_{2(aq)}->SnO^2-_{3(aq)} + Bi^_{(s)}(basic)}\]
Which of the following is INCORRECT for the following reaction?
\[\ce{2Zn_{(s)} + O2_{(g)} -> 2ZnO_{(s)}}\]
Identify coefficients 'x' and 'y' for the following reaction.
\[\ce{{x}H2O2_{(aq)} + ClO^-_{4(aq)} -> 2O2_{(g)} + ClO^-_{2(aq)} + {y}H2O_{(l)}}\]
Which of the following is a redox reaction?
Identify the oxidising agent in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH4_{(g)} + 2O2_{(g)} -> CO2_{(g)} + 2H2O_{(l)}}\]
When methane is burnt completely, oxidation state of carbon changes from ______.
Write balanced chemical equation for the following reactions:
Permanganate ion \[\ce{(MnO^{-}4)}\] reacts with sulphur dioxide gas in acidic medium to produce \[\ce{Mn^{2+}}\] and hydrogen sulphate ion.
Write balanced chemical equation for the following reactions:
Dichlorine heptaoxide \[\ce{(Cl2O7)}\] in gaseous state combines with an aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide in acidic medium to give chlorite ion \[\ce{(ClO^{-}2)}\] and oxygen gas. (Balance by ion-electron method)
Balance the following equations by the oxidation number method.
\[\ce{I2 + NO^{-}3 -> NO2 + IO^{-}3}\]
Balance the following equations by the oxidation number method.
\[\ce{I2 + S2O^{2-}3 -> I- + S4O^{2-}6}\]
Balance the following equations by the oxidation number method.
\[\ce{MnO2 + C2O^{2-}4 -> Mn^{2+} + CO2}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{3HCl (aq) + HNO3 (aq) -> Cl2 (g) + NOCl (g) + 2H2O (l)}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{HgCl2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) -> HgI2 (s) + 2KCl (aq)}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{PCl3 (l) + 3H2O (l) -> 3HCl (aq) + H3PO3 (aq)}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{4NH3 (g) + 3O2 (g) -> 2N2 (g) + 6H2O (g)}\]
Balance the following ionic equations.
\[\ce{Cr2O^{2-}7 + H^{+} + I- -> Cr^{3+} + I2 + H2O}\]
Balance the following ionic equations.
\[\ce{MnO^{-}4 + H^{+} + Br^{-} -> Mn^{2+} + Br2 + H2O}\]
In acidic medium, reaction, \[\ce{MNO^-_4 → Mn^2+}\] an example of ____________.
