Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Choose the correct statements(s):
पर्याय
A dimensionally correct equation may be correct.
A dimensionally correct equation may be incorrect.
A dimensionally incorrect equation may be correct.
A dimensionally incorrect equation may be incorrect.
उत्तर
A dimensionally correct equation may be correct.
A dimensionally correct equation may be incorrect.
A dimensionally incorrect equation may be incorrect.
It is not possible that a dimensionally incorrect equation is correct. All the other situations are possible.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A dimensionless quantity
Choose the correct statements(s):
(a) All quantities may be represented dimensionally in terms of the base quantities.
(b) A base quantity cannot be represented dimensionally in terms of the rest of the base quantities.
(c) The dimensions of a base quantity in other base quantities is always zero.
(d) The dimension of a derived quantity is never zero in any base quantity.
Find the dimensions of electric field E.
The relevant equations are \[F = qE, F = qvB, \text{ and }B = \frac{\mu_0 I}{2 \pi a};\]
where F is force, q is charge, v is speed, I is current, and a is distance.
Find the dimensions of Planck's constant h from the equation E = hv where E is the energy and v is the frequency.
Let I = current through a conductor, R = its resistance and V = potential difference across its ends. According to Ohm's law, product of two of these quantities equals the third. Obtain Ohm's law from dimensional analysis. Dimensional formulae for R and V are \[{\text{ML}}^2 \text{I}^{- 2} \text{T}^{- 3}\] and \[{\text{ML}}^2 \text{T}^{- 3} \text{I}^{- 1}\] respectively.
Test if the following equation is dimensionally correct:
\[v = \frac{1}{2 \pi}\sqrt{\frac{mgl}{I}};\]
where h = height, S = surface tension, \[\rho\] = density, P = pressure, V = volume, \[\eta =\] coefficient of viscosity, v = frequency and I = moment of interia.
Is a vector necessarily changed if it is rotated through an angle?
Is it possible to add two vectors of unequal magnitudes and get zero? Is it possible to add three vectors of equal magnitudes and get zero?
Can you add three unit vectors to get a unit vector? Does your answer change if two unit vectors are along the coordinate axes?
The x-component of the resultant of several vectors
(a) is equal to the sum of the x-components of the vectors of the vectors
(b) may be smaller than the sum of the magnitudes of the vectors
(c) may be greater than the sum of the magnitudes of the vectors
(d) may be equal to the sum of the magnitudes of the vectors.
Let \[\vec{a} = 4 \vec{i} + 3 \vec{j} \text { and } \vec{b} = 3 \vec{i} + 4 \vec{j}\]. Find the magnitudes of (a) \[\vec{a}\] , (b) \[\vec{b}\] ,(c) \[\vec{a} + \vec{b} \text { and }\] (d) \[\vec{a} - \vec{b}\].
Two vectors have magnitudes 2 m and 3m. The angle between them is 60°. Find (a) the scalar product of the two vectors, (b) the magnitude of their vector product.
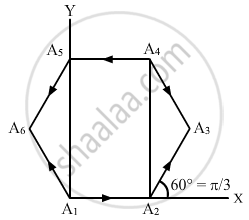
Let A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A1 be a regular hexagon. Write the x-components of the vectors represented by the six sides taken in order. Use the fact the resultant of these six vectors is zero, to prove that
cos 0 + cos π/3 + cos 2π/3 + cos 3π/3 + cos 4π/3 + cos 5π/3 = 0.
Use the known cosine values to verify the result.
Prove that \[\vec{A} . \left( \vec{A} \times \vec{B} \right) = 0\].
If \[\vec{A} = 2 \vec{i} + 3 \vec{j} + 4 \vec{k} \text { and } \vec{B} = 4 \vec{i} + 3 \vec{j} + 2 \vec{k}\] find \[\vec{A} \times \vec{B}\].
Give an example for which \[\vec{A} \cdot \vec{B} = \vec{C} \cdot \vec{B} \text{ but } \vec{A} \neq \vec{C}\].
Draw a graph from the following data. Draw tangents at x = 2, 4, 6 and 8. Find the slopes of these tangents. Verify that the curve draw is y = 2x2 and the slope of tangent is \[\tan \theta = \frac{dy}{dx} = 4x\]
\[\begin{array}x & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 & 5 & 6 & 7 & 8 & 9 & 10 \\ y & 2 & 8 & 18 & 32 & 50 & 72 & 98 & 128 & 162 & 200\end{array}\]
