Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider a metal exposed to light of wavelength 600 nm. The maximum energy of the electron doubles when light of wavelength 400 nm is used. Find the work function in eV.
उत्तर
Work function (or threshold energy) (W0): The minimum energy of incident radiation required to eject the electrons from the metallic surface is defined as the work function of that surface.
W0 = hv0 = `(hc)/λ_0` Joules; v0 = Threshold frequency; λ0 = Threshold wavelength
Work function in electron volt, W0(eV) = `(hc)/(eλ_0) = 12375/(λ_0(Å))`
Einstein's photoelectric equation is E = W0 + Kmax
Maximum energy = `hv - phi`
According to the problem for the first condition wavelength of light λ = 600 nm and for the second condition, the wavelength of light λ' = 400 nm
Also, the maximum kinetic energy for the second condition is equal to twice the kinetic energy in the first condition.
i.e., K'max = 2Kmax
then K'max = `(hc)/λ - phi`
⇒ 2Kmax = `(hc)/λ^' - phi`
⇒ `2(1230/600 - phi) = (1230/400 - phi)` ......[∵ hc = 1240 eV nm]
⇒ `phi = 1230/1230` = 1.02 eV
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use the same formula you employ in (a) to obtain electron speed for an collector potential of 10 MV. Do you see what is wrong? In what way is the formula to be modified?
If the frequency of light in a photoelectric experiment is doubled, the stopping potential will ______.
Calculate the momentum of a photon of light of wavelength 500 nm.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Calculate the number of photons emitted per second by a 10 W sodium vapour lamp. Assume that 60% of the consumed energy is converted into light. Wavelength of sodium light = 590 nm
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A sphere of radius 1.00 cm is placed in the path of a parallel beam of light of large aperture. The intensity of the light is 0.5 W cm−2. If the sphere completely absorbs the radiation falling on it, Show that the force on the sphere due to the light falling on it is the same even if the sphere is not perfectly absorbing.
Find the maximum magnitude of the linear momentum of a photoelectron emitted when a wavelength of 400 nm falls on a metal with work function 2.5 eV.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
When a metal plate is exposed to a monochromatic beam of light of wavelength 400 nm, a negative potential of 1.1 V is needed to stop the photo current. Find the threshold wavelength for the metal.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
The electric field associated with a light wave is given by `E = E_0 sin [(1.57 xx 10^7 "m"^-1)(x - ct)]`. Find the stopping potential when this light is used in an experiment on photoelectric effect with the emitter having work function 1.9 eV.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Define the term: threshold frequency
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
| The figure shows the variation of photoelectric current measured in a photocell circuit as a function of the potential difference between the plates of the photocell when light beams A, B, C and D of different wavelengths are incident on the photocell. Examine the given figure and answer the following questions: |
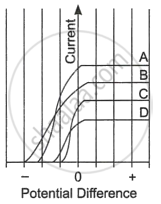
- Which light beam has the highest frequency and why?
- Which light beam has the longest wavelength and why?
- Which light beam ejects photoelectrons with maximum momentum and why?
