Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A sphere of radius 1.00 cm is placed in the path of a parallel beam of light of large aperture. The intensity of the light is 0.5 W cm−2. If the sphere completely absorbs the radiation falling on it, Show that the force on the sphere due to the light falling on it is the same even if the sphere is not perfectly absorbing.
उत्तर
Consider a sphere of centre O and radius OP. As shown in the figure, the radius OP of the sphere is making an angle θ with OZ. Let us rotate the radius about OZ to get another circle on the sphere. The part of the sphere between the circle is a ring of area `2pir^2sin θdθ`.
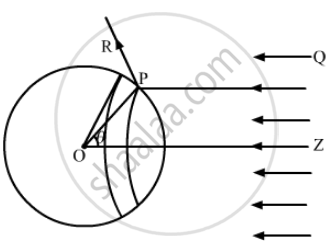
Consider a small part of area `ΔA` of the ring at point P.
Energy of the light falling on this part in time `Δt` ,
`ΔU = I Δ t (ΔA cos θ)`
As the light is reflected by the sphere along PR, the change in momentum ,
`Δp = 2 (ΔU)/c cos θ = 2/c I Δ t (ΔA cos^2 θ)`
Therefore , the force will be
`(Δp)/(Δt) = 2/c I ΔA cos^2 θ`
The Component of force on ΔA , along ZO , is
`(Δp)/(Δt) cos θ = 2/c I ΔA cos^3 θ`
Now , force action on the ring,
`dF = 2/c I (2pir^2 sin θ dθ) cos^3 θ`
The force on the entire sphere ,
`F = ∫_0^(pi/2) (4pir^2I)/c cos^3 θ sin θ dθ`
= `- ∫_0^(pi/2) (4pir^2I)/c cos^3 θd(cos θ)`
= `(pir^2I)/c`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The photoelectric cut-off voltage in a certain experiment is 1.5 V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted?
The following graph shows the variation of photocurrent for a photosensitive metal :
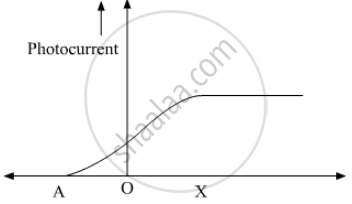
(a) Identify the variable X on the horizontal axis.
(b) What does the point A on the horizontal axis represent?
(c) Draw this graph for three different values of frequencies of incident radiation v1, v2 and v3 (v1 > v2 > v3) for same intensity.
(d) Draw this graph for three different values of intensities of incident radiation I1, I2 and I3 (I1 > I2 > I3) having same frequency.
Can we find the mass of a photon by the definition p = mv?
Can a photon be deflected by an electric field? Or by a magnetic field?
Should the energy of a photon be called its kinetic energy or its internal energy?
The threshold wavelength of a metal is λ0. Light of wavelength slightly less than λ0 is incident on an insulated plate made of this metal. It is found that photoelectrons are emitted for some time and after that the emission stops. Explain.
Two photons of
The work function of a metal is hv0. Light of frequency v falls on this metal. Photoelectric effect will take place only if
When stopping potential is applied in an experiment on photoelectric effect, no photoelectric is observed. This means that
If the frequency of light in a photoelectric experiment is doubled, the stopping potential will ______.
If the wavelength of light in an experiment on photoelectric effect is doubled,
(a) photoelectric emission will not take place
(b) photoelectric emission may or may not take place
(c) the stopping potential will increase
(d) the stopping potential will decrease
In which of the following situations, the heavier of the two particles has smaller de Broglie wavelength? The two particles
(a) move with the same speed
(b) move with the same linear momentum
(c) move with the same kinetic energy
(d) have fallen through the same height
When the sun is directly overhead, the surface of the earth receives 1.4 × 103 W m−2 of sunlight. Assume that the light is monochromatic with average wavelength 500 nm and that no light is absorbed in between the sun and the earth's surface. The distance between the sun and the earth is 1.5 × 1011 m. (a) Calculate the number of photons falling per second on each square metre of earth's surface directly below the sun. (b) How many photons are there in each cubic metre near the earth's surface at any instant? (c) How many photons does the sun emit per second?
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A 100 W light bulb is placed at the centre of a spherical chamber of radius 20 cm. Assume that 60% of the energy supplied to the bulb is converted into light and that the surface of the chamber is perfectly absorbing. Find the pressure exerted by the light on the surface of the chamber.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
When a metal plate is exposed to a monochromatic beam of light of wavelength 400 nm, a negative potential of 1.1 V is needed to stop the photo current. Find the threshold wavelength for the metal.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
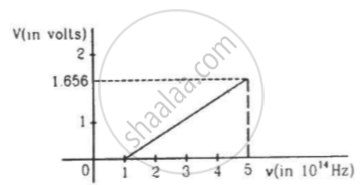
The figure is the plot of stopping potential versus the frequency of the light used in an experiment on photoelectric effect. Find (a) the ratio h/e and (b) the work function.
In photoelectric effect, the photoelectric current started to flow. This means that the frequency of incident radiations is ______.
Do all the electrons that absorb a photon come out as photoelectrons?
Consider a 20 W bulb emitting light of wavelength 5000 Å and shining on a metal surface kept at a distance 2 m. Assume that the metal surface has work function of 2 eV and that each atom on the metal surface can be treated as a circular disk of radius 1.5 Å.
- Estimate no. of photons emitted by the bulb per second. [Assume no other losses]
- Will there be photoelectric emission?
- How much time would be required by the atomic disk to receive energy equal to work function (2 eV)?
- How many photons would atomic disk receive within time duration calculated in (iii) above?
- Can you explain how photoelectric effect was observed instantaneously?
If photons of ultraviolet light of energy 12 eV are incident on a metal surface of work function of 4 eV, then the stopping potential (in eV) will be :
