Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Do all the electrons that absorb a photon come out as photoelectrons?
उत्तर
The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons (called photo-electrons when light strikes a surface. To escape from the surface, the electron must absorb enough energy from the incident radiation to overcome the attraction of positive ions in the material of the surface.
The photoelectric effect is based on the principle of conservation of energy.
1. Two conducting electrodes, the anode (Q) and cathode (P) are enclosed in an evacuated glass tube as shown on next page.
2. The battery or other source of potential difference creates an electric field in the direction from anode to cathode.
3. Light of a certain wavelength or frequency falling on the surface of the cathode causes a current in the external circuit called photoelectric current.
4. As the potential difference increases, photoelectric current also increases till saturation is reached.
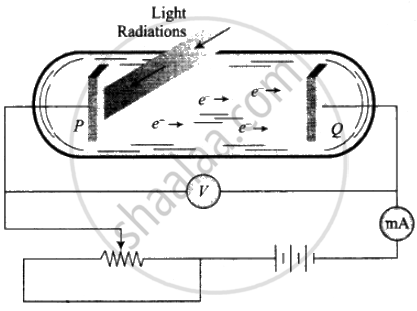
5. When polarity of the battery is reversed (i.e., plate Q is at negative potential w.r.t. plate P) electrons start moving back towards the cathode.
6. At a particular negative potential of plate Q, no electron will reach the plate Q and the current will become zero. This negative potential is called stopping potential denoted by V0. Maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons in terms of stopping potential will therefore be Kmax = (|V0|) eV
So we conclude that in the photoelectric effect, we can observe that most electrons get scattered into the metal by absorbing a photon.
Therefore, all the electrons that absorb a photon don't come out as photoelectron. Only a few come out of metal whose energy becomes greater than the work function of the metal.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the term 'intensity of radiation' in terms of photon picture of light.
The photoelectric cut-off voltage in a certain experiment is 1.5 V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted?
(a) Estimate the speed with which electrons emitted from a heated emitter of an evacuated tube impinge on the collector maintained at a potential difference of 500 V with respect to the emitter. Ignore the small initial speeds of the electrons. The specific charge of the electron, i.e., its e/m is given to be 1.76 × 1011 C kg−1.
(b) Use the same formula you employ in (a) to obtain electron speed for an collector potential of 10 MV. Do you see what is wrong? In what way is the formula to be modified?
A mercury lamp is a convenient source for studying frequency dependence of photoelectric emission, since it gives a number of spectral lines ranging from the UV to the red end of the visible spectrum. In our experiment with rubidium photo-cell, the following lines from a mercury source were used:
λ1 = 3650 Å, λ2 = 4047 Å, λ3 = 4358 Å, λ4 = 5461 Å, λ5 = 6907 Å,
The stopping voltages, respectively, were measured to be:
V01 = 1.28 V, V02 = 0.95 V, V03 = 0.74 V, V04 = 0.16 V, V05 = 0 V
Determine the value of Planck’s constant h, the threshold frequency and work function for the material.
[Note: You will notice that to get h from the data, you will need to know e (which you can take to be 1.6 × 10−19 C). Experiments of this kind on Na, Li, K, etc. were performed by Millikan, who, using his own value of e (from the oil-drop experiment) confirmed Einstein’s photoelectric equation and at the same time gave an independent estimate of the value of h.]
Can we find the mass of a photon by the definition p = mv?
It is found that photosynthesis starts in certain plants when exposed to sunlight, but it does not start if the plants are exposed only to infrared light. Explain.
The threshold wavelength of a metal is λ0. Light of wavelength slightly less than λ0 is incident on an insulated plate made of this metal. It is found that photoelectrons are emitted for some time and after that the emission stops. Explain.
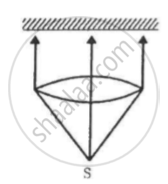
A totally reflecting, small plane mirror placed horizontally faces a parallel beam of light, as shown in the figure. The mass of the mirror is 20 g. Assume that there is no absorption in the lens and that 30% of the light emitted by the source goes through the lens. Find the power of the source needed to support the weight of the mirror.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Define the term: threshold frequency
Answer the following question.
Plot a graph of photocurrent versus anode potential for radiation of frequency ν and intensities I1 and I2 (I1 < I2).
