Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
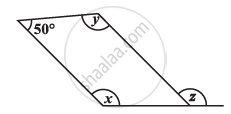
Consider the given parallelogram. Find the values of the unknowns x, y, z.
उत्तर
50° + y = 180° (Adjacent angles are supplementary)
y = 130°
x = y = 130° (Opposite angles are equal)
z = x = 130º (Corresponding angles)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
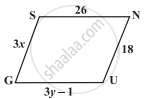
The following figure GUNS is a parallelogram. Find x and y. (Lengths are in cm)
If the ratio of measures of two adjacent angles of a parallelogram is 1 : 2, find the measures of all angles of the parallelogram.
In the given figure, G is the point of concurrence of medians of ΔDEF. Take point H on ray DG such that D-G-H and DG = GH, then prove that `square`GEHF is a parallelogram.

Construct ☐ PQRS, such that l(PQ) = 3.5 cm, l(QR) = 5.6 cm, l(RS) = 3.5 cm, m∠Q = 110°, m∠R = 70°. If it is given that ☐ PQRS is a parallelogram, which of the given information is unnecessary?
PQRS is a parallelogram whose diagonals intersect at M.
If ∠PMS = 54°, ∠QSR = 25° and ∠SQR = 30° ; find :
(i) ∠RPS
(ii) ∠PRS
(iii) ∠PSR.
In the given figure, AB || EC, AB = AC and AE bisects ∠DAC. Prove that:
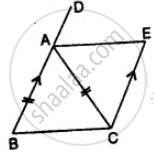
- ∠EAC = ∠ACB
- ABCE is a parallelogram.
The angle between the two altitudes of a parallelogram through the same vertex of an obtuse angle of the parallelogram is 30°. The measure of the obtuse angle is ______.
The adjacent sides of a parallelogram are 5 cm and 9 cm. Its perimeter is ______.
ABCD is a parallelogram. The bisector of angle A intersects CD at X and bisector of angle C intersects AB at Y. Is AXCY a parallelogram? Give reason.
Draw a rough figure of a quadrilateral that is not a parallelogram but has exactly two opposite angles of equal measure.
