Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Diagram is given below shows velocity – time graph of car P and Q, starting from the same place and in the same direction. Calculate which car is ahead after 10 s and by how much?

उत्तर

Distance covered by car P = area of ΔOAB
= `1/2xx"OB"xx"AB"`
= `1/2xx10xx35`
= 175 m
Distance covered by car Q = area of ΔCDE + area of rectangle DFBE
= `1/2xx"CE"xx"DE"+"EB"xx"BF"`
= `1/2xx(5-2)xx25+(10-5)xx25`
= `75/2+125`
= 37.5 + 125
= 162.5 m
So, car P is a head of car Q by (175 − 162.5) m
i.e. by 12.5 m
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What can you say about the motion of a body if its speed-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis ?
Draw a velocity-time graph to show the following motion :
A car accelerates uniformly from rest for 5 s ; then it travels at a steady’ velocity for 5 s.
Show by using the graphical method that: `s=ut+1/2at^2` where the symbols have their usual meanings.
What type of motion is represented by the following graph ?
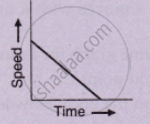
A car of mass 1000 kg is moving with a velocity of 10 m s−1. If the velocity-time graph for this car is a horizontal line parallel to the time axis, then the velocity of car at the end of 25 s will be :
Multiple choice Question. Select the correct option.
What does the area of an acceleration – time graph represent?
A train starting from rest picks up a speed of 20 ms−1 in 200 s. It continues to move at the same rate for the next 500 s and is then brought to rest in another 100 s.
- Plot a speed-time graph.
- From graph calculate
(a) uniform rate of acceleration
(b) uniform rate of retardation
(c) total distance covered before stopping
(d) average speed.
From the velocity – time graph given below, calculate Average velocity in region CED.

Draw velocity-time graph to show:
Zero acceleration
Write a sentence to explain the shape of graph.
Figure shows the distance-time graph of three students A, B and C. On the basis of the graph, answer the following :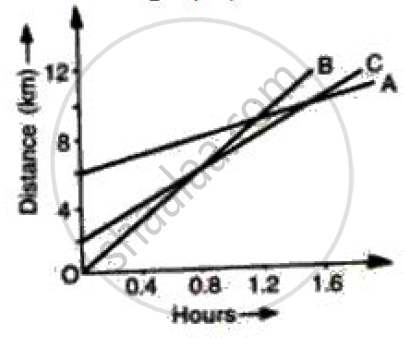
How far did B travel between the time he passed C and A?
