Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a labelled diagram to show different trajectories of a satellite depending upon the tangential projection speed.
उत्तर
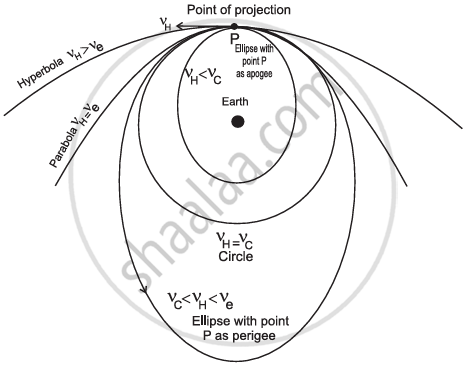
vh = horizontal speed of projection
vc = critical velocity
ve = escape velocity
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A nut becomes loose and gets detached from a satellite revolving around the earth. Will it land on the earth? If yes, where will it land? If no, how can an astronaut make it land on the earth?
Is it necessary for the plane of the orbit of a satellite to pass through the centre of the earth?
No part of India is situated on the equator. Is it possible to have a geostationary satellite which always remains over New Delhi?
As the earth rotates about its axis, a person living in his house at the equator goes in a circular orbit of radius equal to the radius of the earth. Why does he/she not feel weightless as a satellite passenger does?
Two satellites going in equatorial plane have almost same radii. As seen from the earth one moves from east one to west and the other from west to east. Will they have the same time period as seen from the earth? If not which one will have less time period?
Two satellites A and B move round the earth in the same orbit. The mass of B is twice the mass of A.
The radius of a planet is R1 and a satellite revolves round it in a circle of radius R2. The time period of revolution is T. Find the acceleration due to the gravitation of the planet at its surface.
Answer the following question.
Define the binding energy of a satellite.
Answer the following question.
What is periodic time of a geostationary satellite?
Answer the following question in detail.
State any four applications of a communication satellite.
Answer the following question in detail.
Obtain an expression for the binding energy of a satellite revolving around the Earth at a certain altitude.
Solve the following problem.
Calculate the value of acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Mars if the radius of Mars = 3.4 × 103 km and its mass is 6.4 × 1023 kg.
The ratio of energy required to raise a satellite of mass 'm' to a height 'h' above the earth's surface of that required to put it into the orbit at same height is ______.
[R = radius of the earth]
Two satellites of a planet have periods of 32 days and 256 days. If the radius of the orbit of the former is R, the orbital radius of the Latter is ______
Which of the following statements is CORRECT in respect of a geostationary satellite?
There is no atmosphere on moon because ____________.
An aircraft is moving with uniform velocity 150 m/s in the space. If all the forces acting on it are balanced, then it will ______.
Two satellites of masses m1 and m2 (m1 > m2) are revolving round the earth in circular orbit of radii r1 and r2 (r1 > r2) respectively. Which of the following statements is true regarding their speeds v1 and v2?
Reason of weightlessness in a satellite is ____________.
A satellite of mass 'm', revolving round the earth of radius 'r' has kinetic energy (E). Its angular momentum is ______.
A satellite is revolving in a circular orbit around the earth has total energy 'E'. Its potential energy in that orbit is ______.
A geostationary satellite is orbiting the earth at a height 6R above the surface of the earth, where R is the radius of the earth. This time period of another satellite at a height (2.5 R) from the surface of the earth is ______.
Show the nature of the following graph for a satellite orbiting the earth.
- KE vs orbital radius R
- PE vs orbital radius R
- TE vs orbital radius R.
An artificial satellite is moving in a circular orbit around the earth with a speed equal to half the magnitude of escape velocity from the earth. If the satellite is stopped in its orbit and allowed to fall freely onto the earth, the speed with which it hits the surface ______ km/s.
[g = 9.8 ms-2 and Re = 6400 km]
A satellite revolves around a planet very close to its surface. By what maximum factor can its kinetic energy be increased suddenly, such that it revolves in orbit in the same way?
A satellite is revolving around a planet in a circular orbit close to its surface and ρ is the mean density and R is the radius of the planet, then the period of ______.
(G = universal constant of gravitation)
