Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw a labelled diagram to show different trajectories of a satellite depending upon the tangential projection speed.
Solution
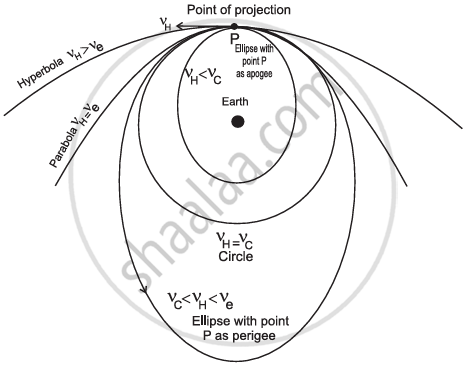
vh = horizontal speed of projection
vc = critical velocity
ve = escape velocity
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Suppose there existed a planet that went around the sun twice as fast as the earth.What would be its orbital size as compared to that of the earth?
Consider earth satellites in circular orbits. A geostationary satellite must be at a height of about 36000 km from the earth's surface. Will any satellite moving at this height be a geostationary satellite? Will any satellite moving at this height have a time period of 24 hours?
No part of India is situated on the equator. Is it possible to have a geostationary satellite which always remains over New Delhi?
A spacecraft consumes more fuel in going from the earth to the moon than it takes for a return trip. Comment on this statement.
At what rate should the earth rotate so that the apparent g at the equator becomes zero? What will be the length of the day in this situation?
What is the true weight of an object in a geostationary satellite that weighed exactly 10.0 N at the north pole?
Choose the correct option.
The binding energy of a satellite revolving around the planet in a circular orbit is 3 × 109 J. It's kinetic energy is ______.
Answer the following question.
What do you mean by geostationary satellite?
Answer the following question.
What is periodic time of a geostationary satellite?
Answer the following question.
Why is a minimum two-stage rocket necessary for launching of a satellite?
Derive an expression for the critical velocity of a satellite.
Answer the following question in detail.
Why an astronaut in an orbiting satellite has a feeling of weightlessness?
Answer the following question in detail.
Obtain an expression for the binding energy of a satellite revolving around the Earth at a certain altitude.
Describe how an artificial satellite using a two-stage rocket is launched in an orbit around the Earth.
A planet has mass 6.4 × 1024 kg and radius 3.4 × 106 m. Calculate the energy required to remove an object of mass 800 kg from the surface of the planet to infinity.
Two satellites of a planet have periods of 32 days and 256 days. If the radius of the orbit of the former is R, the orbital radius of the Latter is ______
Which of the following statements is CORRECT in respect of a geostationary satellite?
The kinetic energy of a revolving satellite (mass m) at a height equal to thrice the radius of the earth (R) is ______.
What is the minimum energy required to launch a satellite of mass 'm' from the surface of the earth of mass 'M' and radius 'R' at an altitude 2R?
An aircraft is moving with uniform velocity 150 m/s in the space. If all the forces acting on it are balanced, then it will ______.
If a body weighing 40 kg is taken inside the earth to a depth to radius of the earth, then `1/8`th the weight of the body at that point is ______.
Reason of weightlessness in a satellite is ____________.
Assuming that the earth is revolving around the sun in circular orbit of radius 'R', the angular momentum is directly proportional to rn. The value of 'n' is ______.
If the Earth-Sun distance is held constant and the mass of the Sun is doubled, then the period of revolution of the earth around the Sun will change to ____________.
A geostationary satellite is orbiting the earth at a height 6R above the surface of the earth, where R is the radius of the earth. This time period of another satellite at a height (2.5 R) from the surface of the earth is ______.
A satellite revolves around a planet very close to its surface. By what maximum factor can its kinetic energy be increased suddenly, such that it revolves in orbit in the same way?
