Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
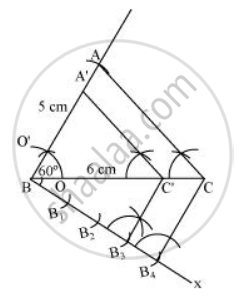
Draw a triangle ABC with BC = 6 cm, AB = 5 cm and ∠ABC = 60°. Then construct a triangle whose sides are `3/4` of the corresponding sides of the ∆ABC.
उत्तर
A ΔA'BC' whose sides are `3/4`of the corresponding sides of ΔABC can be drawn as follows:
Step 1
Draw a ΔABC with side BC = 6 cm, AB = 5 cm and ∠ABC = 60°
Step 2
Draw a ray BX making an acute angle with BC on the opposite side of vertex A.
Step 3
Locate 4 points (as 4 is greater in 3 and 4), B1, B2, B3, B4, on line segment BX.
Step 4
Join B4C and draw a line through B3, parallel to B4C intersecting BC at C'
Step 5
Draw a line through C' parallel to AC intersecting AB at A'. ΔA'BC' is the required triangle.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Construct an isosceles triangle whose base is 6 cm and altitude 4 cm. Then construct another triangle whose sides are `3/4`times the corresponding sides of the isosceles triangle.
Construct a ΔABC with BC = 7 cm, ∠B = 60° and AB = 6 cm. Construct another triangle whose sides are `3/4` times the corresponding sides of ΔABC
Construct a ΔABC in which AB = 6 cm, ∠A = 30° and ∠AB = 60° . Construct another ΔAB'C ' similar to ΔABC with base AB’ = 8 cm.
Construct a ΔABC in which BC = 8 cm, ∠B = 45° and ∠C = 60° . Construct another triangle similar to ΔABC such that its sides are `3/5`of the corresponding sides of ΔABC .
To construct a triangle similar to ΔABC in which BC = 4.5 cm, ∠B = 45° and ∠C =60° , using a scale factor of `3/7`, BC will be divided in the ratio
(a) 3 : 4 (b) 4 : 7 (c) 3 : 10 (d) 3 : 7
Construct an isosceles triangles whose base is 8 cm and altitude 4 cm and then another triangle whose sides are`1/2` times the corresponding sides of the isosceles triangle.
Construct a triangle with sides 5 cm, 5.5 cm and 6.5 cm. Now construct another triangle, whose sides are \[\frac{3}{5}\] times the corresponding sides of the given triangle.
Construct a triangle PQR with sides QR = 7 cm, PQ = 6 cm and \[\angle\]PQR = 60º. Then construct another triangle whose sides are \[\frac{3}{5}\] of the corresponiding sides of ∆PQR.
Draw a ∆ABC in which base BC = 6 cm, AB = 5 cm and ∠ABC = 60°. Then construct another triangle whose sides are \[\frac{3}{4}\] of the corresponding sides of ∆ABC.
The line segment joining the points A(2, 1) and B(5, −8) is trisected at the points P and Q such that P is nearer to A. If P also lies on the line given by 2x − y + k = 0, find the value of k.
