Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain [Fe(CN)6]3− is an inner orbital complex, whereas [FeF6]3− is an outer orbital complex.
[Atomic number: Fe = 26]
उत्तर
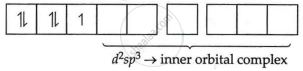
[Fe(CN)6]3−
Fe = 3 oxidation state
i.e., electronic configuration = 3d5
CNΘ = strong field ligand
i.e., Δ0 > P pairing will take place
Electronic configuration of Fe3+ = 3d5
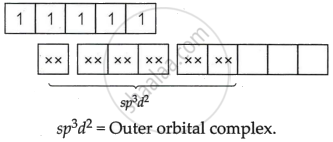
[FeF6]3−
Fe = +3 oxidation state
F− = Weak field ligand Δ0 < P `->` Pairing will not take place.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
For the complex [Fe(H2O)6]+3, write the hybridisation, magnetic character and spin of the complex. (At, number : Fe = 26)
For the complex [Fe(CN)6]3–, write the hybridization type, magnetic character and spin nature of the complex. (At. number : Fe = 26).
Write the hybridization and shape of the following complexe : [Ni(CN)4]2–
(Atomic number : Co = 27, Ni = 28)
Amongst the following ions, which one has the highest magnetic moment value?
Write the hybridization and magnetic character of the following complexes:
[Fe(H2O)6]2+
(Atomic no. of Fe = 26)
Write the hybridization and magnetic character of the following complexes:
[Fe(CO)5]
(Atomic no. of Fe = 26)
Which of the following options are correct for \[\ce{[Fe(CN)6]^{3-}}\] complex?
(i) d2sp3 hybridisation
(ii) sp3d2 hybridisation
(iii) paramagnetic
(iv) diamagnetic
Explain why \[\ce{[Fe(H2O)6]^{3+}}\] has magnetic moment value of 5.92 BM whereas \[\ce{[Fe(CN)6]^{3-}}\] – has a value of only 1.74 BM.
Why do compounds having similar geometry have different magnetic moment?
The correct order of magnetic moment (spin only value in B.m.) is
