Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain geometry of methane molecule on the basis of Hybridization.
उत्तर
Formation of methane (CH4) molecule on the basis of sp3 hybridization:
- Methane molecule (CH4) has one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms.
- The ground state electronic configuration of C (Z = 6) is 1s2 2s2 \[\ce{2p^1_{{x}}}\] \[\ce{2p^1_{{y}}}\] \[\ce{2p^0_{{z}}}\].
Electronic configuration of carbon:
Ground state: 1s 2s 2p ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ ↑ Excited state:
1s 2s 2p ↑↓ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ sp3 Hybrid orbitals: ↑↓ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ 1s (four sp3 hybrid orbitals) - In order to form four equivalent bonds with hydrogen, the 2s and 2p orbitals of C-atom undergo sp3 hybridization.
- One electron from the 2s orbital of the carbon atom is excited to the 2pz orbital. Then the four orbitals 2s, px, py, and pz mix and recast to form four new sp3 hybrid orbitals having the same shape and equal energy. They are maximum apart and have tetrahedral geometry with an H–C–H bond angle of 109°28'. Each hybrid orbital contains one unpaired electron.
- Each of these sp3 hybrid orbitals with one electron overlaps axially with the 1s orbital of the hydrogen atom to form one C–H sigma bond. Thus, in CH4 molecule, there are four C–H bonds formed by the sp3–s overlap.
Diagram:
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the formation of H2 molecule on the basis of valence bond theory.
Draw diagram for bonding in ethene with sp2 Hybridisation.
Distinguish between sigma and pi bond.
Display electron distribution around the oxygen atom in the water molecule and state the shape of the molecule, also write the H-O-H bond angle.
Give a reason for the sigma (σ) bond is stronger than the Pi (π) bond.
Give a reason for carbon is tetravalent in nature.
Identify the type of overlap present in H2. Explain diagrammatically.
Identify the type of overlap present in H-F molecule. Explain diagrammatically.
Complete the following Table.
| Molecule | Type of Hybridization | Type of bonds | Geometry | Bond angle |
| CH4 | - | 4C-H 4σ bonds |
Tetrahedral | - |
| NH3 | sp3 | 3N-H 3σ bonds 1 lone pair |
- | - |
| H2O | - | - | angular | 104.5° |
| BF3 | sp2 | - | - | 120° |
| C2H4 | - | - | - | 120° |
| BeF2 | - | 2 Be-F | Linear | - |
| C2H2 | sp | (3σ+2π) 1C-C σ 2C-H σ 2C-C π |
- | - |
Give the type of overlap by which the pi (π) bond is formed.
Mention the steps involved in Hybridization.
The ratio of number of sigma (σ) and pi (л) bonds in 2- butynal is ______.
Among the following, the compound that contains, ionic, covalent and Coordinate linkage is ______.
Considering x-axis as the molecular axis which out of the following will form a sigma bond.
2px and 2py
Considering x-axis as the molecular axis which out of the following will form a sigma bond.
1s and 2pz
Which of the following is correct decreasing order of the repulsive Interaction of electron pairs in a molecule?
The number of sigma bonds in paracetamol is ____________.
The number of sigma bonds in vanillin is ____________.
Why does type of overlap given in the following figure not result in bond formation?
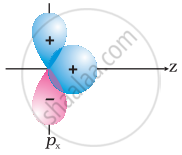 |
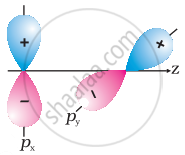 |
Briefly describe the valence bond theory of covalent bond formation by taking an example of hydrogen. How can you interpret energy changes taking place in the formation of dihydrogen?
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT according to the valence bond theory?
The \[\ce{H - N - H}\] bond angle in ammonia molecule is ______.
