Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain why carbon forms compounds mainly by covalent bond.
उत्तर
Carbon has 4 electrons in its outermost shell and requires 4 more electrons to attain a noble gas electronic configuration. It cannot form a C4+ ion, as the removal of 4 valence electrons requires a huge amount of energy. The C4+ ion thus formed will have 6 protons and 2 electrons, which will make it highly unstable. Carbon cannot form a C4− ion, as its nucleus with 6 protons cannot hold 10 electrons due to inter electronic repulsion. So, carbon achieves a noble gas electronic configuration only by sharing its 4 valence electrons with other elements. Thus, it forms compounds mainly by covalent bonds.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw the electron-dot structure of a hydrogen chloride molecule.
Explain why, diamond is hard while graphite is soft (though both are made of carbon atoms).
Draw the electron-dot structure of NH3 and state the type of bonding.
What do you understand by polar covalent compounds?
Draw an electron dot diagram for the formation of the following. State the type of bonding present in them.
Hydroxyl ion
Explain the following term with example.
Hetero atom in a carbon compound
Write answer as directed.
What causes the existance of very large number of carbon compound ?
The following structural formula belongs to which carbon compound?
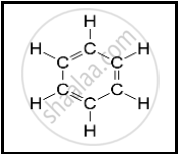
Give examples for the following:
Two solid covalent compounds.
Explain the structure of Ammonium ion.
State the type of bonding in the following molecule.
Water
In the formation of electrovalent compounds, electrons are transferred from one element to another. How are electrons involved in the formation of a covalent compound?
Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statement:
Covalent compounds are generally soluble in _________ solvents.
Name two carbon compounds used in day-to-day life.
Write scientific reason.
Benzene compounds are called aromatic compounds.
Complete the following activity.
Write the names of the hydrocarbons for the following structural formula.
(isobutylene, cyclohexane, propene, cyclohexene, cyclopentane, benzene, propyne, isobutane, propane)
| \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{..}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\ \phantom{..}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\ \ce{H - C - C- C- H}\\ \phantom{.}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\ \ce{H - C - H}\\ |\\\ce{H}\end{array}\] |
Give an example for each of the following statement.
Formation of coordinate covalent bond between NH3 ➝ BF3 molecules
The I.U.P.A.C name of CH3CH2CH = CH2 is?
Molecular reactions are ______ in the covalent compound.
