Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Figure shows a boy pulling a wagon on a road. List as many forces as you can which are relevant with this figure. Find the pairs of forces connected by Newton's third law of motion.
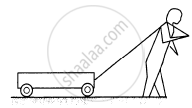
उत्तर
List of forces :
(a) A pair of gravitational force between the wagon and the Earth.
(b) A frictional force exerted by the road on the wagon.
(c) A tension exerts electromagnetic force between the wagon and string.
(d) A pair of gravitational force between the man and the Earth.
(e) A frictional force exerted by the road on the man.
(f) A tension exerts electromagnetic force between the man and string.
Here, (a), (c), (d) and (f) are pairs of forces associated with Newton's third law of motion.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Let E, G and N represent the magnitudes of electromagnetic gravitational and nuclear forces between two electrons at a given separation. Then
A proton exerts a force on a proton which is
(a) gravitational
(b) electromagnetic
(c) nuclear
(d) weak
Calculate the force with which you attract the earth.
A body builder exerts a force of 150 N against a bullworker and compresses it by 20 cm. Calculate the spring constant of the spring in the bullworker.
The force with which the earth attracts an object is called the weight of the object. Calculate the weight of the moon from the following data : The universal constant of gravitation G = 6.67 × 11−11 N−m2/kg2, mass of the moon = 7.36 × 1022 kg, mass of the earth = 6 × 1024 kg and the distance between the earth and the moon = 3.8 × 105 km.
The work done by all the forces (external and internal) on a system equals the change in ______.
A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is always perpendicular to the velocity of the plane. The motion of the particle takes place in a plane. It follows that
(a) its velocity is constant
(b) its acceleration is constant
(c) its kinetic energy is constant
(d) it moves in a circular path.
No work is done by a force on an object if
(a) the force is always perpendicular to its velocity
(b) the force is always perpendicular to its acceleration
(c) the object is stationary but the point of application of the force moves on the object
(d) the object moves in such a way that the point of application of the force remains fixed.
A particle moves from a point \[\overrightarrow{r}_1 = \left( 2 m \right) \overrightarrow{ i } + \left( 3 m \right) \overrightarrow{ j } \] to another point
\[\overrightarrow{r}_2 = \left( 3 m \right) \overrightarrow{ i } + \left( 2 m \right) \overrightarrow{ j } \] acts on it. Find the work done by the force on the particle during the displacement.
A block of mass 250 g slides down an incline of inclination 37° with uniform speed. Find the work done against friction as the block slides through 1m.
A block of mass 2 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclination 37° is pulled up the plane by applying a constant force of 20 N parallel to the incline. The force acts for one second. Show that the work done by the applied force does not exceed 40 J.
A block of mass 2 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclination 37° is pulled up the plane by applying a constant force of 20 N parallel to the incline. The force acts for one second. Find the work done by the force of gravity in that one second if the work done by the applied force is 40 J.
A block of mass 2 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclination 37° is pulled up the plane by applying a constant force of 20 N parallel to the incline. The force acts for one second. Find the kinetic energy of the block at the instant the force ceases to act. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A uniform chain of length L and mass M overhangs a horizontal table with its two third part on the table. The friction coefficient between the table and the chain is μ . Find the work done by friction during the period the chain slips off the table.
The work done by an applied variable force, F = x + x3 from x = 0 m to x = 2m, where x is displacement, is:
A bicyclist comes to a skidding stop in 10 m. During this process, the force on the bicycle due to the road is 200 N and is directly opposed to the motion. The work done by the cycle on the road is ______.
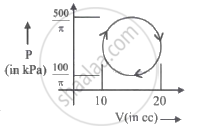
Work done by gas in cyclic process is ______ J.
Force acting on a particle is (2`hat"i"` + 3 `hat"j"`) N. Work done by this force is zero, when a particle is moved on the line 3y + kx = 5. Here value of k is ______.
A body is displaced from (0, 0) to (1 m, 1 m) along the path x = y by a force F = (x2`hat"J"` + y`hat"i"`)N. The work done by this force will be:
