Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For the travelling harmonic wave
y (x, t) = 2.0 cos 2π (10t – 0.0080x + 0.35)
Where x and y are in cm and t in s. Calculate the phase difference between oscillatory motion of two points separated by a distance of `(3λ)/4`.
उत्तर १
Equation for a travelling harmonic wave is given as:
y (x, t) = 2.0 cos 2π (10t – 0.0080x + 0.35)
= 2.0 cos (20πt – 0.016πx + 0.70 π)
Where,
Propagation constant, k = 0.0160 π
Amplitude, a = 2 cm
Angular frequency, ω= 20 π rad/s
Phase difference is given by the relation:
`phi = kx = (2pi)/lambda`
For `x = (3lambda)/4`
`phi = (2pi)/lambda xx (3lambda)/4`
`= 1.5 pi` rad
उत्तर २
The given equation can be drawn be rewritten as under
y(x, t) `= 2.0 cos [2pi (10"t" - 0.0080x) + 2pi xx 0.35]`
or y(x, t) `= 2.0 cos [2pi xx 0.0080((10"t")/0.0080 - x) + 0.7pi]`
Comparing this equation with the standard equation of a travelling harmonic wave.
`(2pi)/lambda = 2pi xx 0.0080` or `lambda = 1/0.0080 "cm" = 125` cm
The phase difference between oscillatory motion of two points seperated by a distance `trianglex` is given by
`trianglephi = (2pi)/lambda trianglex`
When `trianglex = (3lambda)/4 = (3xx125)/4` cm, then
`triangle phi = (2phi)/125 xx (3xx125)/4`
`= (3pi)/2 "rad"`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A steel wire has a length of 12.0 m and a mass of 2.10 kg. What should be the tension in the wire so that speed of a transverse wave on the wire equals the speed of sound in dry air at 20 °C = 343 m s–1.
For the wave described in Exercise 15.8, plot the displacement (y) versus (t) graphs for x = 0, 2 and 4 cm. What are the shapes of these graphs? In which aspects does the oscillatory motion in travelling wave differ from one point to another: amplitude, frequency or phase?
A train, standing at the outer signal of a railway station blows a whistle of frequency 400 Hz in still air. (i) What is the frequency of the whistle for a platform observer when the train (a) approaches the platform with a speed of 10 m s–1, (b) recedes from the platform with a speed of 10 m s–1? (ii) What is the speed of sound in each case? The speed of sound in still air can be taken as 340 m s–1.
A SONAR system fixed in a submarine operates at a frequency 40.0 kHz. An enemy submarine moves towards the SONAR with a speed of 360 km h–1. What is the frequency of sound reflected by the submarine? Take the speed of sound in water to be 1450 m s–1.
Two sine waves travel in the same direction in a medium. The amplitude of each wave is A and the phase difference between the two waves is 120°. The resultant amplitude will be
The equation of a wave travelling on a string is \[y = \left( 0 \cdot 10 \text{ mm } \right) \sin\left[ \left( 31 \cdot 4 m^{- 1} \right)x + \left( 314 s^{- 1} \right)t \right]\]
(a) In which direction does the wave travel? (b) Find the wave speed, the wavelength and the frequency of the wave. (c) What is the maximum displacement and the maximum speed of a portion of the string?
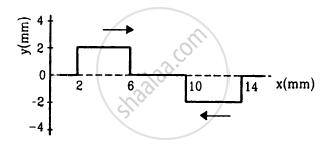
Following figure shows two wave pulses at t = 0 travelling on a string in opposite directions with the same wave speed 50 cm s−1. Sketch the shape of the string at t = 4 ms, 6 ms, 8 ms, and 12 ms.
A 2⋅00 m-long rope, having a mass of 80 g, is fixed at one end and is tied to a light string at the other end. The tension in the string is 256 N. (a) Find the frequencies of the fundamental and the first two overtones. (b) Find the wavelength in the fundamental and the first two overtones.
Use the formula `v = sqrt((gamma P)/rho)` to explain why the speed of sound in air increases with temperature.
A sound wave is passing through air column in the form of compression and rarefaction. In consecutive compressions and rarefactions ______.
