Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
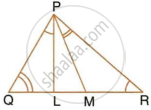
In a triangle PQR, L and M are two points on the base QR, such that ∠LPQ = ∠QRP and ∠RPM = ∠RQP. Prove that:
- ΔPQL ∼ ΔRPM
- QL × RM = PL × PM
- PQ2 = QR × QL
उत्तर
i. In ΔPQL and ΔRMP
∠LPQ = ∠QRP ...(Given)
∠RQP = ∠RPM ...(Given)
ΔPQL ∼ ΔRMP ...(AA similarity)
ii. As ΔPQL ∼ ΔRMP ...(Proved above)
`(PQ)/(RP) = (QL)/(PM) = (PL)/(RM)`
`=>` QL × RM = PL × PM
iii. ∠LPQ = ∠QRP ...(Given)
∠Q = ∠Q ...(Common)
∆PQL ∼ ∆RQP ...(AA similarity)
= `(PQ)/(RQ) = (QL)/(QP) = (PL)/(PR) `
`=>` PQ2 = QR × QL
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
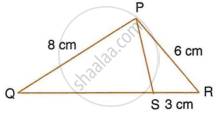
PQR is a triangle. S is a point on the side QR of ΔPQR such that ∠PSR = ∠QPR. Given QP = 8 cm, PR = 6 cm and SR = 3 cm.
- Prove ΔPQR ∼ ΔSPR.
- Find the length of QR and PS.
- `"area of ΔPQR"/"area of ΔSPR"`
Given: ABCD is a rhombus, DPR and CBR are straight lines.
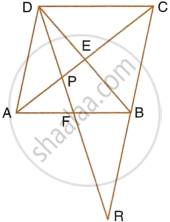
Prove that: DP × CR = DC × PR.
In ∆ ABC, ∠B = 2 ∠C and the bisector of angle B meets CA at point D. Prove that:
(i) ∆ ABC and ∆ ABD are similar,
(ii) DC: AD = BC: AB
In ∆PQR, ∠Q = 90° and QM is perpendicular to PR. Prove that:
- PQ2 = PM × PR
- QR2 = PR × MR
- PQ2 + QR2 = PR2
In the right-angled triangle QPR, PM is an altitude.
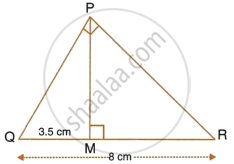
Given that QR = 8 cm and MQ = 3.5 cm, calculate the value of PR.
In the given triangle PQR, LM is parallel to QR and PM : MR = 3 : 4.
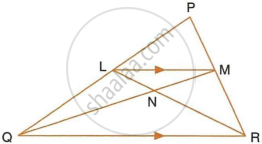
Calculate the value of ratio:
- `(PL)/(PQ)` and then `(LM)/(QR)`
- `"Area of ΔLMN"/"Area of ΔMNR"`
- `"Area of ΔLQM"/"Area of ΔLQN"`
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle. DE is parallel to BC and `(AD)/(DB)=3/2`
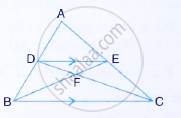
(1) Determine the ratios `(AD)/(AB) and (DE)/(BC)`
(2 ) Prove that ∆DEF is similar to ∆CBF Hence, find `(EF)/(FB)`.
(3) What is the ratio of the areas of ∆DEF and ∆BFC.
An aeroplane is 30 m long and its model is 15 cm long. If the total outer surface area of the model is 150 cm2, find the cost of painting the outer surface of the aeroplane at the rate of Rs.120 per sq. m. Given that 50 sq. m of the surface of the aeroplane is left for windows.
The dimensions of the model of a multistoreyed building are 1 m by 60 cm by 1.20 m. If the scale factor is 1 : 50, find the actual dimensions of the building.
Also, find:
- the floor area of a room of the building, if the floor area of the corresponding room in the model is 50 sq. cm.
- the space (volume) inside a room of the model, if the space inside the corresponding room of the building is 90 m3.
A triangle ABC with AB = 3 cm, BC = 6 cm and AC = 4 cm is enlarged to ΔDEF such that the longest side of ΔDEF = 9 cm. Find the scale factor and hence, the lengths of the other sides of ΔDEF.
