Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In an alternating current circuit consisting of elements in series, the current increases on increasing the frequency of supply. Which of the following elements are likely to constitute the circuit?
- Only resistor.
- Resistor and an inductor.
- Resistor and a capacitor.
- Only a capacitor.
पर्याय
b and c
a and d
b and d
c and d
उत्तर
c and d
Explanation:
This is a similar problem as we discussed above. In this problem, the current increases on increasing the frequency of supply. Hence, the reactance of the circuit must be decreased as increase in frequency. So, one element that must be connected is the capacitor. We can also connect a resistor in series.
For a capacitive circuit,
XC = 1/ωC = 1/2πfC
When frequency increases, XC decreases. Hence current in the circuit increases.
Important point: Resistive, Capacitive CIrcuit (RC - Circuit)
VR = iR,
VC = iXC,
VR = iR
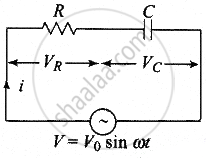
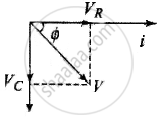
- Applied voltage: `V = sqrt(V_R^2 + V_C^2)`
- Impedance: `Z = sqrt(R^2 + X_C^2) = sqrt(R^2 + (1/(ωC)^2)`
- Current: `i = i_0 sin(ωt + phi)`
- Peak current: `I_0 = V_0/Z = V_0/sqrt(R^2 + X_C^2) = V_0/sqrt(R^2 + 1/(4pi^2v^2C^2)`
- Phase difference: `phi = tan^-1 X_C/R = tan^-1 1/(ωCR)`
- Power factor: `cos phi = R/sqrt(R^2 + X_C^2)`
- Leading quantity: Current
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Derive an expression for phase angle between the applied voltage and current in a series RLC circuit.
Define capacitive reactance. Give its units.
Obtain an expression for average power of AC over a cycle. Discuss its special cases.
In any ac circuit, is the applied instantaneous voltage equal to the algebraic sum of the instantaneous voltages across the series elements of the circuit? Is the same true for rms voltage?
Why is choke coil needed in the use of fluorescent tubes with ac mains? Why can we not use an ordinary resistor instead of the choke coil?
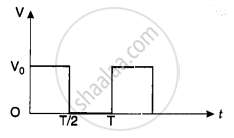
The rms value of potential difference V shown in the figure is ______.
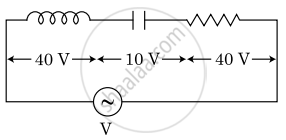
An inductor of inductance L, a capacitor of capacitance C and a resistor of resistance ‘R’ are connected in series to an ac source of potential difference ‘V’ volts as shown in figure. Potential difference across L, C and R is 40 V, 10 V and 40 V, respectively. The amplitude of current flowing through LCR series circuit is `10sqrt2` A. The impedance of the circuit is :
For a series LCR circuit, I vs ω curve is shown:
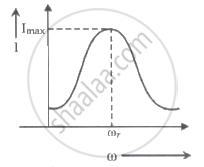
- To the left of ωr, the circuit is mainly capacitive.
- To the left of ωr, the circuit is mainly inductive.
- At ωr, impedance of the circuit is equal to the resistance of the circuit.
- At ωr, impedance of the circuit is 0.
An alternating voltage v(t) = 220 sin 100πt volt is applied to a purely resistive load of 50 Ω. The time taken for the current to rise from half of the peak value to the peak value is ______.
State any one difference between a direct current (dc) and an alternating current (ac).
