Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In dealing with motion of projectile in air, we ignore effect of air resistance on motion. This gives trajectory as a parabola as you have studied. What would the trajectory look like if air resistance is included? Sketch such a trajectory and explain why you have drawn it that way.
उत्तर
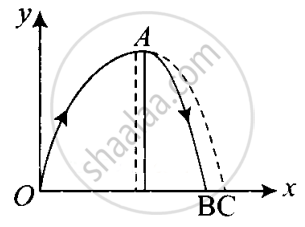
When we are dealing with projectile motion generally we neglect air resistance. But if air resistance is included the horizontal component of velocity will not be constant and obviously trajectory will change.
Due to air resistance, particle energy as well as the horizontal component of velocity keep on decreasing making the fall steeper than the rise as shown in the figure.
When we are neglecting the air resistance path was symmetric parabola (OAC). When air resistance is considered path is an asymmetric parabola (OAB).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A body of mass m is projected horizontally with a velocity v from the top of a tower of height h and it reaches the ground at a distance x from the foot of the tower. If the second body of mass of 4 m is projected horizontally from the top of a tower of the height of 4 h, it reaches the ground at a distance of 4x from the foot of the tower. The horizontal velocity of the second body is:
A ball rolls of the top of the stairway with a horizontal velocity u ms−1. If the steps are h m high and b m wide, the ball will hit the edge of the nth step, if:
A particle moving in a circle of radius R with a uniform speed takes a time T to complete one revolution.
If this particle were projected with the same speed at an angle ‘θ’ to the horizontal, the maximum height attained by it equals 4R. The angle of projection, θ, is then given by ______.
A car starts from rest and accelerates at 5 m/s2. At t = 4 s, a ball is dropped out of a window by a person sitting in the car. What is the velocity and acceleration of the ball at t = 6 s? (Take g = 10 m/s2)
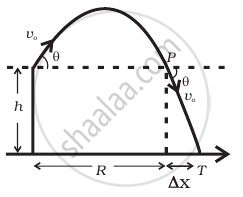
A gun can fire shells with maximum speed v0 and the maximum horizontal range that can be achieved is R = `v_0^2/g`. If a target farther away by distance ∆x (beyond R) has to be hit with the same gun (Figure), show that it could be achieved by raising the gun to a height at least `h = Δx[ 1 + (Δx)/R]`
A particle is projected in air at an angle β to a surface which itself is inclined at an angle α to the horizontal (Figure).
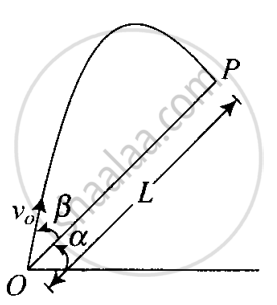
- Find an expression of range on the plane surface (distance on the plane from the point of projection at which particle will hit the surface).
- Time of flight.
- β at which range will be maximum.
A girl riding a bicycle with a speed of 5 m/s towards north direction, observes rain falling vertically down. If she increases her speed to 10 m/s, rain appears to meet her at 45° to the vertical. What is the speed of the rain? In what direction does rain fall as observed by a ground based observer?
A football is kicked into the air vertically upwards. What is its velocity at the highest point?
Two stones are projected with the same speed but making different angles with the horizontal. Their ranges are equal. If the angle of projection of one is `pi/3` and its maximum height is y1 then the maximum height of the other will be ______.
The initial speed of a bullet fired from a rifle is 630 m/s. The rifle is fired at the centre of a target 700 m away at the same level as the target. How far above the centre of the target the rifle must be aimed in order to hit the target?
