Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
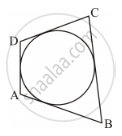
In Figure 3, a circle touches all the four sides of a quadrilateral ABCD whose sides are AB = 6 cm, BC = 9 cm and CD = 8 cm. Find the length of the side AD.
उत्तर
Let the inscribed circle touch sides AB, BC, CD and DA of quadrilateral ABCD at P, Q, R and S respectively.
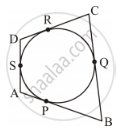
It is known that the lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.
∴ AS = AP, DS = DR, BP = BQ, CR = CQ
AD
= AS + DS
= AP + DR
= (6 − PB) + (8 − CR)
= 14 cm − BQ − CQ [(Using (1)]
= 14 cm − (BQ + CQ)
= 14 cm − BC
= (14 − 9) cm
= 5 cm
Thus, the length of side AD is 5 cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
true or false
The degree measure of an arc is the complement of the central angle containing the arc.
In the below fig. O is the centre of the circle. If ∠APB = 50°, find ∠AOB and ∠OAB.

In the adjoining figure, a circle touches all the four sides of a quadrilateral ABCD whose sides are AB=6cm, BC=9cm and CD=8 cm. Find the length of side AD.
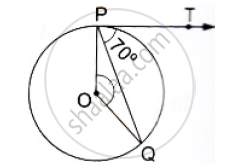
If PT is a tangent to a circle with center O and PQ is a chord of the circle such that ∠QPT = 70°, then find the measure of ∠POQ.
One chord of a circle is known to be 10 cm. The radius of this circle must be
In the given figure, the area enclosed between the two concentric circles is 770 cm2. If the radius of the outer circle is 21 cm, calculate the radius of the inner circle.
If O is the centre of the circle, find the value of x in each of the following figures

Construct a triangle ABC with AB = 4.2 cm, BC = 6 cm and AC = 5cm. Construct the circumcircle of the triangle drawn.
Find the diameter of the circle
Radius = 8 cm
In the given figure, AB is the diameter of the circle. Find the value of ∠ACD.