Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In figure, PQ ⊥ RQ, PQ = 5 cm and QR = 5 cm. Then ∆PQR is ______.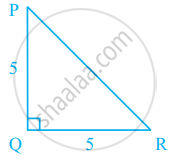
पर्याय
A right triangle but not isosceles
An isosceles right triangle
Isosceles but not a right triangle
Neither isosceles nor right triangle
उत्तर
In figure, PQ ⊥ RQ, PQ = 5 cm and QR = 5 cm. Then ∆PQR is an isosceles right triangle.
Explanation:
Since, PQ Perpendicular to RQ
So, ∆PQR = 90°
∴ ∆PQR is right-angled triangle.
Also, in ΔPQR,
PQ = QR
ΔPQR is an isosceles triangle.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
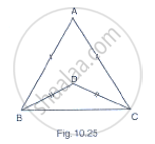
In Fig. 10.25, AB = AC and DB = DC, find the ratio ∠ABD : ∠ACD.
In Δ ABC, BD⊥ AC and CE ⊥ AB. If BD and CE intersect at O, prove that ∠BOC = 180° − A.
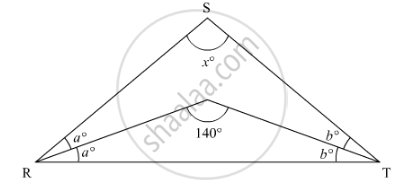
In ΔRST (See figure), what is the value of x?
Find the value of the angle in the given figure:

Find x, if the angles of a triangle is:
x°, x°, x°
Find x, if the angles of a triangle is:
x°, 2x°, 2x°
The length of the three segments is given for constructing a triangle. Say whether a triangle with these sides can be drawn. Give the reason for your answer.
7 cm, 24 cm, 25 cm
The correct statement out of the following is 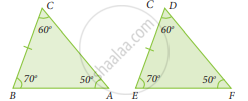
In a ∆ABC, AB = AC. The value of x is ________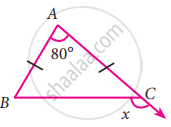
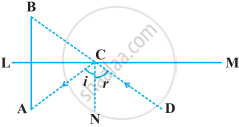
The image of an object placed at a point A before a plane mirror LM is seen at the point B by an observer at D as shown in the following figure. Prove that the image is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror.
[Hint: CN is normal to the mirror. Also, angle of incidence = angle of reflection].