Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the following Figure, ∠ABC = 90° and BD ⊥ AC. If BD = 8 cm and AD = 4 cm, find CD.
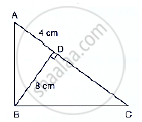
उत्तर
We have, ∠ABC = 90° and BD ⊥ AC
Now, ∠ABD + ∠DBC − 90° …(i) [∵ ∠ABC − 90°]
And, ∠C + ∠DBC − 90° …(ii) [By angle sum prop. in ΔBCD]
Compare equations (i) & (ii)
∠ABD = ∠C …(iii)
In ΔABD and ΔBCD
∠ABD = ∠C [From (iii)]
∠ADB = ∠BDC [Each 90°]
Then, ΔABD ~ ΔBCD [By AA similarity]
`therefore"BD"/"CD"="AD"/"BD"` [Corresponding parts of similar Δ are proportional]
`rArr8/"CD"=4/8`
`rArr"CD"=(8xx8)/4=16` cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
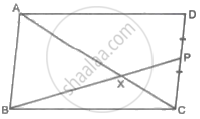
In the following figure, altitudes AD and CE of ΔABC intersect each other at the point P. Show that:
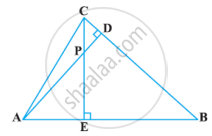
ΔABD ∼ ΔCBE
A vertical stick 10 cm long casts a shadow 8 cm long. At the same time a shadow 30 m long. Determine the height of the tower.
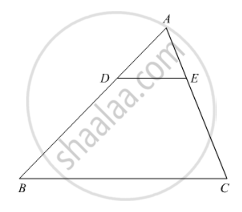
In the following Figure, DE || BC such that AE = (1/4) AC. If AB = 6 cm, find AD.
Two triangles DEF an GHK are such that ∠D = 48° and ∠H = 57° . If ΔDEF ∼GHK then find the measures of ∠F
In figure, if DE || BC, find the ratio of ar(ADE) and ar(DECB).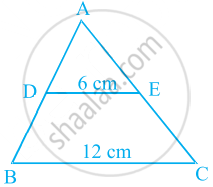
It is given that ΔABC ~ ΔDFE, ∠A =30°, ∠C = 50°, AB = 5 cm, AC = 8 cm and DF = 7.5 cm. Then, the following is true ______.
□ABCD is a parallelogram. Point P is the midpoint of side CD. seg BP intersects diagonal AC at point X, then prove that: 3AX = 2AC
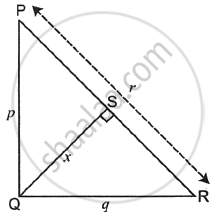
In the given figure, ΔPQR is a right-angled triangle with ∠PQR = 90°. QS is perpendicular to PR. Prove that pq = rx.
In the given figure, ΔLMN is similar to ΔPQR. To find the measure of ∠N, complete the following activity.
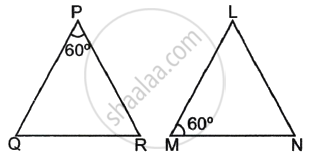
Given: ΔLMN ∼ ΔPQR
Since ΔLMN ∼ ΔPQR, therefore, corresponding angles are equal.
So, ∠L ≅ `square`
⇒ ∠L = `square`
We know, the sum of angles of a triangle = `square`
∴ ∠L + ∠M + ∠N = `square`
Substituting the values of ∠L and ∠M in equation (i),
`square` + `square` + ∠N = `square`
∠N + `square` = `square`
∠N = `square` – `square`
∠N = `square`
Hence, the measure of ∠N is `square`.
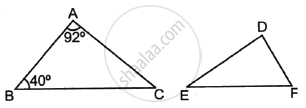
If ΔABC ∼ ΔDEF such that ∠A = 92° and ∠B = 40°, then ∠F = ?