Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In parallelogram ABCD, the angle bisector of ∠A bisects BC. Will angle bisector of B also bisect AD? Give reason.
उत्तर
Given, ABCD is a parallelogram, bisector of ∠A, bisects BC at F, i.e. ∠1 = ∠2, CF = FB.
Draw FE || BA.
ABFE is a parallelogram by construction ...[∵ FE || BA]
⇒ ∠1 = ∠6 ...[Alternate angle]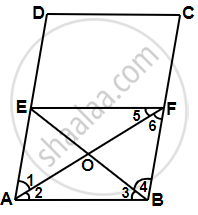
But ∠1 = ∠2 ...[Given]
∴ ∠2 = ∠6
AB = FB [Opposite sides to equal angles are equal] ...(i)
∴ ABFE is a rhombus.
Now, In ΔABO and ΔBOF,
AB = BF ...[From equation (i)]
BO = BO ...[Common]
AO = FO ...[Diagonals of rhombus bisect each other]
∴ ΔABO ≅ ΔBOF ...[By SSS]
∠3 = ∠4 ...[By CPCT]
Now, BF = `1/2` BC ...[Given]
⇒ BF = `1/2` AD ...[BC = AD]
⇒ AE = `1/2` AD ...[BF = AE]
∴ E is the midpoint of AD.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Consider the given parallelogram. Find the values of the unknowns x, y, z.

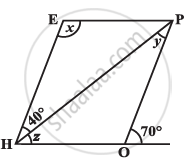
The adjacent figure HOPE is a parallelogram. Find the angle measures x, y and z. State the properties you use to find them.
In the given figure, AB || EC, AB = AC and AE bisects ∠DAC. Prove that:
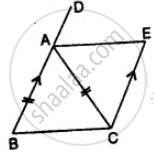
- ∠EAC = ∠ACB
- ABCE is a parallelogram.
Iron rods a, b, c, d, e, and f are making a design in a bridge as shown in the figure. If a || b, c || d, e || f, find the marked angles between d and e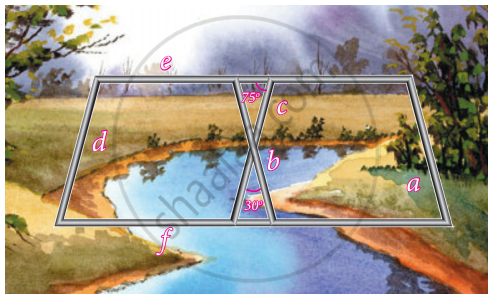
All rectangles are parallelograms.
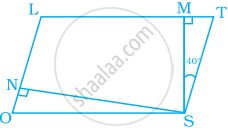
In parallelogram LOST, SN ⊥ OL and SM ⊥ LT. Find ∠STM, ∠SON and ∠NSM.
In parallelogram MODE, the bisector of ∠M and ∠O meet at Q, find the measure of ∠MQO.
ABCD is a parallelogram. The bisector of angle A intersects CD at X and bisector of angle C intersects AB at Y. Is AXCY a parallelogram? Give reason.
A diagonal of a parallelogram bisects an angle. Will it also bisect the other angle? Give reason.
ABCD is a parallelogram. Points P and Q are taken on the sides AB and AD respectively and the parallelogram PRQA is formed. If ∠C = 45°, find ∠R.
