Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the given fig, bisectors of ∠B and ∠C of ∆ABC intersect each other in point X. Line AX intersects side BC in point Y. AB = 5, AC = 4, BC = 6 then find `"AX"/"XY"`.

उत्तर
In Δ ABY,
ray BX bisects ∠ABY ...(Given)
∴ by the theorem of an angle bisector of a triangle,
`("AB")/("BY") = ("AX")/("XY")` ...(1)
In Δ ACY,
ray CX bisects ∠ACY ...(Given)
∴ by the theorem of an angle bisector of a triangle,
`("AC")/("CY") = ("AX")/("XY")` ...(2)
`("AB")/("BY") = ("AC")/("CY") = ("AX")/("XY")` ...[From (1) and (2)]
∴ `5/("BY") = 4/("CY") = ("AX")/("XY")`
By theorem on equal ratios,
`(5 + 4)/("BY" + "CY") = ("AX")/("XY")`
∴ `9/("BC") = ("AX")/("XY")` ...(B - Y - C)
∴ `9/6 = ("AX")/("XY")`
∴ `("AX")/("XY") = 3/2`
संबंधित प्रश्न
Given below is the triangle and length of line segments. Identify in the given figure, ray PM is the bisector of ∠QPR.

Given below is the triangle and length of line segments. Identify in the given figure, ray PM is the bisector of ∠QPR.

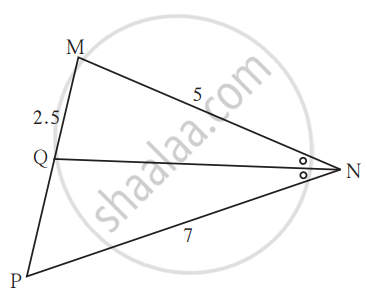
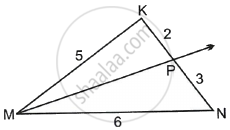
In ∆MNP, NQ is a bisector of ∠N. If MN = 5, PN = 7 MQ = 2.5 then find QP.
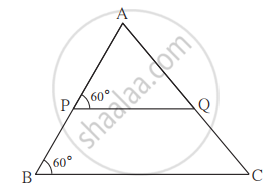
Measures of some angles in the figure are given. Prove that `"AP"/"PB" = "AQ"/"QC"`.
Find QP using given information in the figure.

In the given figure, if AB || CD || FE then find x and AE.

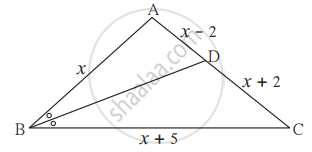
In ∆ABC, seg BD bisects ∠ABC. If AB = x, BC = x + 5, AD = x – 2, DC = x + 2, then find the value of x.
In ∆PQR seg PM is a median. Angle bisectors of ∠PMQ and ∠PMR intersect side PQ and side PR in points X and Y respectively. Prove that XY || QR.

Complete the proof by filling in the boxes.
In △PMQ, ray MX is bisector of ∠PMQ.
∴ `square/square = square/square` .......... (I) theorem of angle bisector.
In △PMR, ray MY is bisector of ∠PMQ.
∴ `square/square = square/square` .......... (II) theorem of angle bisector.
But `(MP)/(MQ) = (MP)/(MR)` .......... M is the midpoint QR, hence MQ = MR.
∴ `(PX)/(XQ) = (PY)/(YR)`
∴ XY || QR .......... converse of basic proportionality theorem.
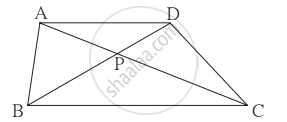
In ▢ABCD, seg AD || seg BC. Diagonal AC and diagonal BD intersect each other in point P. Then show that `"AP"/"PD" = "PC"/"BP"`.

In ΔABC, ray BD bisects ∠ABC.
If A – D – C, A – E – B and seg ED || side BC, then prove that:
`("AB")/("BC") = ("AE")/("EB")`
Proof :
In ΔABC, ray BD bisects ∠ABC.
∴ `("AB")/("BC") = (......)/(......)` ......(i) (By angle bisector theorem)
In ΔABC, seg DE || side BC
∴ `("AE")/("EB") = ("AD")/("DC")` ....(ii) `square`
∴ `("AB")/square = square/("EB")` [from (i) and (ii)]
In ΔABC, ∠ACB = 90°. seg CD ⊥ side AB and seg CE is angle bisector of ∠ACB.
Prove that: `(AD)/(BD) = (AE^2)/(BE^2)`.
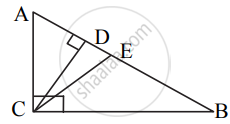
In the following figure, ray PT is the bisector of ∠QPR Find the value of x and perimeter of ∠QPR.
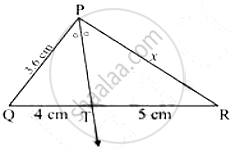
From the information given in the figure, determine whether MP is the bisector of ∠KMN.
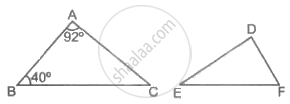
If ΔABC ∼ ΔDEF such that ∠A = 92° and ∠B = 40°, then ∠F = ?
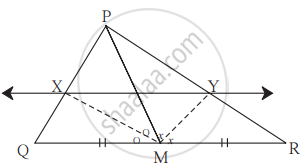
In ∆PQR seg PM is a median. Angle bisectors of ∠PMQ and ∠PMR intersect side PQ and side PR in points X and Y respectively. Prove that XY || QR.
Complete the proof by filling in the boxes.
solution:
In ∆PMQ,
Ray MX is the bisector of ∠PMQ.
∴ `("MP")/("MQ") = square/square` .............(I) [Theorem of angle bisector]
Similarly, in ∆PMR, Ray MY is the bisector of ∠PMR.
∴ `("MP")/("MR") = square/square` .............(II) [Theorem of angle bisector]
But `("MP")/("MQ") = ("MP")/("MR")` .............(III) [As M is the midpoint of QR.]
Hence MQ = MR
∴ `("PX")/square = square/("YR")` .............[From (I), (II) and (III)]
∴ XY || QR .............[Converse of basic proportionality theorem]

In ΔABC, ray BD bisects ∠ABC, A – D – C, seg DE || side BC, A – E – B, then for showing `("AB")/("BC") = ("AE")/("EB")`, complete the following activity:
Proof :
In ΔABC, ray BD bisects ∠B.
∴ `square/("BC") = ("AD")/("DC")` ...(I) (`square`)
ΔABC, DE || BC
∴ `(square)/("EB") = ("AD")/("DC")` ...(II) (`square`)
∴ `("AB")/square = square/("EB")` ...[from (I) and (II)]
