Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In Young’s double slit experiment, how is interference pattern affected when the following changes are made:
- Slits are brought closer to each other.
- Screen is moved away from the slits.
- Red coloured light is replaced with blue coloured light.
उत्तर
- Fringe width (separation) increases.
- Fringe width (separation) increases.
- Fringe width (separation) decreases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a double-slit experiment using the light of wavelength 600 nm, the angular width of the fringe formed on a distant screen is 0.1°. Find the spacing between the two slits.
In a double-slit experiment the angular width of a fringe is found to be 0.2° on a screen placed 1 m away. The wavelength of light used is 600 nm. What will be the angular width of the fringe if the entire experimental apparatus is immersed in water? Take refractive index of water to be 4/3.
A parallel beam of light of wavelength 500 nm falls on a narrow slit and the resulting diffraction pattern is observed on a screen 1 m away. It is observed that the first minimum is a distance of 2.5 mm away from the centre. Find the width of the slit.
A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths, 800 nm and 600 nm is used to obtain the interference fringes in a Young's double slit experiment on a screen placed 1 · 4 m away. If the two slits are separated by 0·28 mm, calculate the least distance from the central bright maximum where the bright fringes of the two wavelengths coincide.
How does the fringe width get affected, if the entire experimental apparatus of Young is immersed in water?
A plate of thickness t made of a material of refractive index µ is placed in front of one of the slits in a double slit experiment. (a) Find the change in the optical path due to introduction of the plate. (b) What should be the minimum thickness t which will make the intensity at the centre of the fringe pattern zero? Wavelength of the light used is \[\lambda.\] Neglect any absorption of light in the plate.
A parallel beam of monochromatic light is used in a Young's double slit experiment. The slits are separated by a distance d and the screen is placed parallel to the plane of the slits. Slow that if the incident beam makes an angle \[\theta = \sin^{- 1} \left( \frac{\lambda}{2d} \right)\] with the normal to the plane of the slits, there will be a dark fringe at the centre P0 of the pattern.
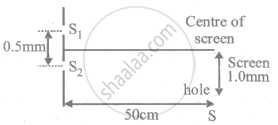
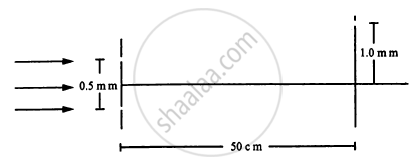
White coherent light (400 nm-700 nm) is sent through the slits of a Young's double slit experiment (see the following figure). The separation between the slits is 0⋅5 mm and the screen is 50 cm away from the slits. There is a hole in the screen at a point 1⋅0 mm away (along the width of the fringes) from the central line. (a) Which wavelength(s) will be absent in the light coming from the hole? (b) Which wavelength(s) will have a strong intensity?
The line-width of a bright fringe is sometimes defined as the separation between the points on the two sides of the central line where the intensity falls to half the maximum. Find the line-width of a bright fringe in a Young's double slit experiment in terms of \[\lambda,\] d and D where the symbols have their usual meanings.
In Young's double slit experiment shown in figure S1 and S2 are coherent sources and S is the screen having a hole at a point 1.0 mm away from the central line. White light (400 to 700 nm) is sent through the slits. Which wavelength passing through the hole has strong intensity?