Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Is it possible for a current loop to stay without rotating in a uniform magnetic field? If yes, what should be the orientation of the loop?
उत्तर
Yes, if the direction of the area vector coincides with the direction of the magnetic field, the torque acting on the loop due to the magnetic field will become zero. Hence, no rotation will be produced in the coil.
It follows from the fact that torque acting on the loop is directly proportional to si θθ, where θθ is the angle made by the area vector with the direction of the magnetic field. So, we can see from this correlation that torque is zero if
θ = 0 or θ = 180°.
`τ = vecm xx vecB`
= mBsin (θ)
⇒ For θ = 0 or integral multiple of π ,
τ = 0
Which implies that the coil will not rotate.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
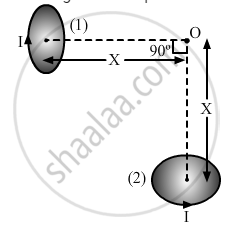
Two very small identical circular loops, (1) and (2), carrying equal currents I are placed vertically (with respect to the plane of the paper) with their geometrical axes perpendicular to each other as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field produced at the point O.
A circular loop of area 1 cm2, carrying a current of 10 A, is placed in a magnetic field of 0.1 T perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The torque on the loop due to the magnetic field is
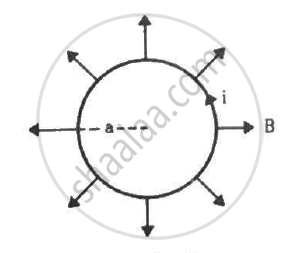
A circular loop of radius a, carrying a current i, is placed in a two-dimensional magnetic field. The centre of the loop coincides with the centre of the field (figure). The strength of the magnetic field at the periphery of the loop is B. Find the magnetic force on the wire.
The figure shows a circular wire loop of radius a and carrying a current i, which is placed in a perpendicular magnetic field B. (a) Consider a small part dl of the wire. Find the force on this part of the wire exerted by the magnetic field. (b) Find the force of compression in the wire.
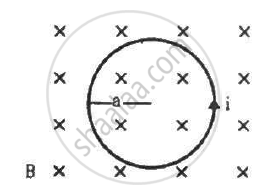
Suppose that the radius of cross-section of the wire used in the previous problem is r. Find the increase in the radius of the loop if the magnetic field is switched off. Young's modulus of the material of the wire is Y.
A rectangular loop of sides 20 cm and 10 cm carries a current of 5.0 A. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.20 T exists parallel to the longer side of the loop. (a) What is the force acting on the loop? (b) What is the torque acting on the loop?
A 50-turn circular coil of radius 2.0 cm carrying a current of 5.0 A is rotated in a magnetic field of strength 0.20 T. (a) What is the maximum torque that acts on the coil? (b) In a particular position of the coil, the torque acting on it is half of this maximum. What is the angle between the magnetic field and the plane of the coil?
Derive an expression for the net torque on a rectangular current carrying loop placed in a uniform magnetic field with its rotational axis perpendicular to the field.
A rectangular coil of length 0.12 m and width 0.1 m having 100 turns of wire is suspended vertically in a uniform magnetic field of strength 0.4 Wb/m2. The coil carries a current of 2.5 A. If the plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of 30° with the direction of the field, the torque required to keep the coil in stable equilibrium will be ____________.
A 100 turn rectangular coil measuring 0.02 m x 0.06 m of an ammeter is in a magnetic field of induction 0.4 tesla. The torsional constant of the suspension fibre is 5 x 10-7 newton x metre/degree. The maximum reading of the ammeter corresponds to a deflection of the coil through 30°. If the magnetic field is radial, then the maximum current that can be measured with this ammeter is ____________.
A small cylindrical soft iron piece is kept in a galvanometer so that
If in a moving coil galvanometer, a current I produces a deflection `theta,` then ____________.
The sensitivity of a milliammeter of range 0 to 50 mA is x `"div"/"mA"`. If it is converted into an ammeter of range 500 mA by using a suitable shunt then the sensitivity will be ________.
Two galvanometers 'G1' and 'G2' require 2 mA and 3 mA respectively to produce the same deflection. Then _______.
If number of turns in moving coil galvanometer becomes half, then the deflection for the same current will become ____________.
The magnetic field developed due to current carrying coil at its centre is 'B'. If the new coil of two turns is prepared from the above coil and same current is passed, then the magnetic field at the centre of the new coil will be ____________.
When the plane of the coil is parallel to the field, torque will be ______
A uniform conducting wire of length 12a and resistance R is wound up as a current-carrying coil in the shape of (i) an equilateral triangle of side a; (ii) a square of sides a and, (iii) a regular hexagon of sides a. The coil is connected to a voltage source V0. Find the magnetic moment of the coils in each case.
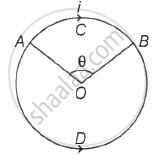
Equal current i flows in two segments of a circular loop in the direction shown in figure. Radius of the loop is r. The magnitude of magnetic field induction at the centre of the loop is ______.
A circular coil having N turns of radius R carrying a current I is used to produce a magnetic field B at its centre O.
If this coil is opened and rewound such that the radius of the newly formed coil is 2R, carrying the same current I, what will be the magnetic field at the centre O?
