Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Let X = {1, 2, 3}and Y = {4, 5}. Find whether the following subset of X ×Y are function from X to Y or not
k = {(1,4), (2, 5)}
उत्तर
Given, X = {1, 2, 3} and Y = {4, 5}
So, X × Y = {(1, 4), (1, 5), (2, 4), (2, 5), (3, 4), (3, 5)}
k = {(1, 4),(2, 5)}
Function k is not a function as ‘3’ has not any image under the mapping.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Let f: R → R be the Signum Function defined as
f(x) = `{(1,x>0), (0, x =0),(-1, x< 0):}`
and g: R → R be the Greatest Integer Function given by g(x) = [x], where [x] is greatest integer less than or equal to x. Then does fog and gof coincide in (0, 1]?
If A = {1, 2, 3}, show that a onto function f : A → A must be one-one.
Find fog (2) and gof (1) when : f : R → R ; f(x) = x2 + 8 and g : R → R; g(x) = 3x3 + 1.
Give examples of two functions f : N → N and g : N → N, such that gof is onto but f is not onto.
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = x+1, g(x) = `e^x`
.
Which of the following graphs represents a one-one function?
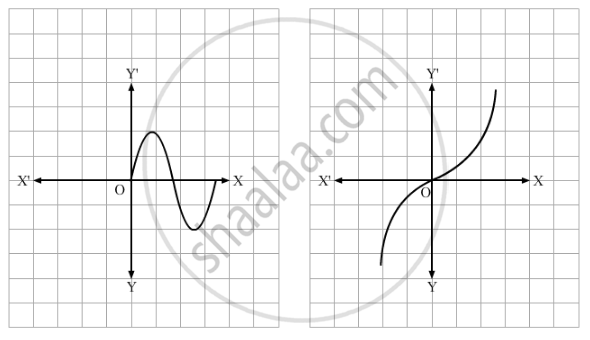
If f : R → R is defined by f(x) = 10 x − 7, then write f−1 (x).
Let A = {x ∈ R : −4 ≤ x ≤ 4 and x ≠ 0} and f : A → R be defined by \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{\left| x \right|}{x}\]Write the range of f.
Let \[f : \left[ - \frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2} \right] \to\] A be defined by f(x) = sin x. If f is a bijection, write set A.
What is the range of the function
`f (x) = ([x - 1])/(x -1) ?`
If f : R → R be defined by f(x) = (3 − x3)1/3, then find fof (x).
If f : {5, 6} → {2, 3} and g : {2, 3} → {5, 6} are given by f = {(5, 2), (6, 3)} and g = {(2, 5), (3, 6)}, then find fog. [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
The function f : R → R defined by
`f (x) = 2^x + 2^(|x|)` is
The function \[f : [0, \infty ) \to \text {R given by } f\left( x \right) = \frac{x}{x + 1} is\]
Let
\[f : R \to R\] be a function defined by
\[f : Z \to Z\] be given by
` f (x) = {(x/2, ", if x is even" ) ,(0 , ", if x is odd "):}`
Then, f is
If \[f\left( x \right) = \sin^2 x\] and the composite function \[g\left( f\left( x \right) \right) = \left| \sin x \right|\] then g(x) is equal to
Let the function f: R → R be defined by f(x) = 4x – 1, ∀ x ∈ R. Then, show that f is one-one.
Let A be a finite set. Then, each injective function from A into itself is not surjective.
Let the function f: R → R be defined by f(x) = cosx, ∀ x ∈ R. Show that f is neither one-one nor onto
Let A = [–1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following functions defined on A are one-one, onto or bijective:
k(x) = x2
Let f: R → R be given by f(x) = tan x. Then f–1(1) is ______.
The function f : A → B defined by f(x) = 4x + 7, x ∈ R is ____________.
The smallest integer function f(x) = [x] is ____________.
Consider a function f: `[0, pi/2] ->` R, given by f(x) = sinx and `g[0, pi/2] ->` R given by g(x) = cosx then f and g are
Let f: R→R be a continuous function such that f(x) + f(x + 1) = 2, for all x ∈ R. If I1 = `int_0^8f(x)dx` and I2 = `int_(-1)^3f(x)dx`, then the value of I1 + 2I2 is equal to ______.
Let x is a real number such that are functions involved are well defined then the value of `lim_(t→0)[max{(sin^-1 x/3 + cos^-1 x/3)^2, min(x^2 + 4x + 7)}]((sin^-1t)/t)` where [.] is greatest integer function and all other brackets are usual brackets.
Let a and b are two positive integers such that b ≠ 1. Let g(a, b) = Number of lattice points inside the quadrilateral formed by lines x = 0, y = 0, x = b and y = a. f(a, b) = `[a/b] + [(2a)/b] + ... + [((b - 1)a)/b]`, then the value of `[(g(101, 37))/(f(101, 37))]` is ______.
(Note P(x, y) is lattice point if x, y ∈ I)
(where [.] denotes greatest integer function)
Let f(x) = ax (a > 0) be written as f(x) = f1(x) + f2(x), where f1(x) is an even function and f2(x) is an odd function. Then f1(x + y) + f1(x – y) equals ______.
