Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A particle moves in the X-Y plane according to the equation \[\overrightarrow{r} = \left( \overrightarrow{i} + 2 \overrightarrow{j} \right)A\cos\omega t .\]
The motion of the particle is
(a) on a straight line
(b) on an ellipse
(c) periodic
(d) simple harmonic
उत्तर
(a) on a straight line
(c) periodic
(d) simple harmonic
The given equation is a solution to the equation of simple harmonic motion. The amplitude is \[( \overrightarrow i + 2 \overrightarrow j)A\] , following equation of straight line y = mx + c. Also, a simple harmonic motion is periodic.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define phase of S.H.M.
Can simple harmonic motion take place in a non-inertial frame? If yes, should the ratio of the force applied with the displacement be constant?
It is proposed to move a particle in simple harmonic motion on a rough horizontal surface by applying an external force along the line of motion. Sketch the graph of the applied force against the position of the particle. Note that the applied force has two values for a given position depending on whether the particle is moving in positive or negative direction.
The force acting on a particle moving along X-axis is F = −k(x − vo t) where k is a positive constant. An observer moving at a constant velocity v0 along the X-axis looks at the particle. What kind of motion does he find for the particle?
A particle moves in a circular path with a continuously increasing speed. Its motion is
Which of the following quantities are always negative in a simple harmonic motion?
(a) \[\vec{F} . \vec{a} .\]
(b) \[\vec{v} . \vec{r} .\]
(c) \[\vec{a} . \vec{r} .\]
(d)\[\vec{F} . \vec{r} .\]
Which of the following quantities are always zero in a simple harmonic motion?
(a) \[\vec{F} \times \vec{a} .\]
(b) \[\vec{v} \times \vec{r} .\]
(c) \[\vec{a} \times \vec{r} .\]
(d) \[\vec{F} \times \vec{r} .\]
A pendulum having time period equal to two seconds is called a seconds pendulum. Those used in pendulum clocks are of this type. Find the length of a second pendulum at a place where g = π2 m/s2.
The pendulum of a certain clock has time period 2.04 s. How fast or slow does the clock run during 24 hours?
A small block oscillates back and forth on a smooth concave surface of radius R ib Figure . Find the time period of small oscillation.
Assume that a tunnel is dug across the earth (radius = R) passing through its centre. Find the time a particle takes to cover the length of the tunnel if (a) it is projected into the tunnel with a speed of \[\sqrt{gR}\] (b) it is released from a height R above the tunnel (c) it is thrown vertically upward along the length of tunnel with a speed of \[\sqrt{gR}\]
Assume that a tunnel is dug along a chord of the earth, at a perpendicular distance R/2 from the earth's centre where R is the radius of the earth. The wall of the tunnel is frictionless. (a) Find the gravitational force exerted by the earth on a particle of mass mplaced in the tunnel at a distance x from the centre of the tunnel. (b) Find the component of this force along the tunnel and perpendicular to the tunnel. (c) Find the normal force exerted by the wall on the particle. (d) Find the resultant force on the particle. (e) Show that the motion of the particle in the tunnel is simple harmonic and find the time period.
Define the time period of simple harmonic motion.
Write short notes on two springs connected in parallel.
Consider the Earth as a homogeneous sphere of radius R and a straight hole is bored in it through its centre. Show that a particle dropped into the hole will execute a simple harmonic motion such that its time period is
T = `2π sqrt("R"/"g")`
A spring is stretched by 5 cm by a force of 10 N. The time period of the oscillations when a mass of 2 kg is suspended by it is ______
The displacement of a particle is represented by the equation `y = 3 cos (pi/4 - 2ωt)`. The motion of the particle is ______.
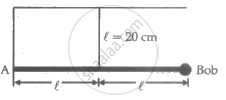
A weightless rigid rod with a small iron bob at the end is hinged at point A to the wall so that it can rotate in all directions. The rod is kept in the horizontal position by a vertical inextensible string of length 20 cm, fixed at its midpoint. The bob is displaced slightly, perpendicular to the plane of the rod and string. The period of small oscillations of the system in the form `(pix)/10` is ______ sec. and the value of x is ______.
(g = 10 m/s2)