Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Plot a graph to show the variation of stopping potential with frequency of incident radiation in relation to photoelectric effect.
उत्तर १
Due to increase in frequency there is increase in K.E. of electron.
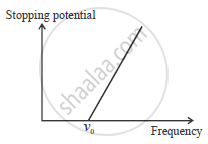
So stopping potential increases with increase in frequency of incides ralation.
उत्तर २
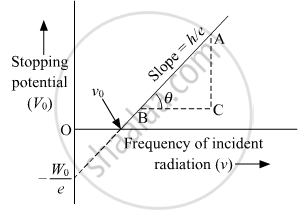
उत्तर ३

संबंधित प्रश्न
An electron gun with its collector at a potential of 100 V fires out electrons in a spherical bulb containing hydrogen gas at low pressure (∼10−2 mm of Hg). A magnetic field of 2.83 × 10−4 T curves the path of the electrons in a circular orbit of radius 12.0 cm. (The path can be viewed because the gas ions in the path focus the beam by attracting electrons, and emitting light by electron capture; this method is known as the ‘fine beam tube’ method. Determine e/m from the data.
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, light of wavelength 400 nm is incident on a cesium plate at the rate of 5.0 W. The potential of the collector plate is made sufficiently positive with respect to the emitter, so that the current reaches its saturation value. Assuming that on average, one out of every 106 photons is able to eject a photoelectron, find the photocurrent in the circuit.
In the arrangement shown in the figure, y = 1.0 mm, d = 0.24 mm and D = 1.2 m. The work function of the material of the emitter is 2.2 eV. Find the stopping potential V needed to stop the photocurrent.
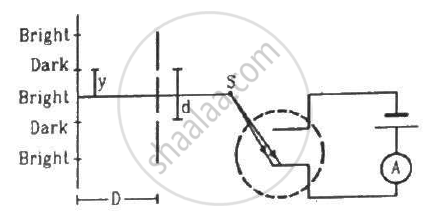
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A silver ball of radius 4.8 cm is suspended by a thread in a vacuum chamber. Ultraviolet light of wavelength 200 nm is incident on the ball for some time during which light energy of 1.0 × 10−7 J falls on the surface. Assuming that on average, one photon out of every ten thousand is able to eject a photoelectron, find the electric potential at the surface of the ball, assuming zero potential at infinity. What is the potential at the centre of the ball?
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
In the case of a photo electric effect experiment, explain the following facts, giving reasons.
The wave theory of light could not explain the existence of the threshold frequency.
In Photoelectric effect ______.
In the experimental set up for studying photoelectric effect, if keeping the frequency of the incident radiation and the accelerating potential fixed, the intensity of light is varied, then ______.
When a beam of 10.6 eV photons of intensity 2.0 W/m2 falls on a platinum surface of area 1.0 × 10-4 m2, only 53% of the incident photons eject photoelectrons. The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is ______.
Cathode rays can be deflected by
In photoelectric effect, the photoelectric current
