Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, light of wavelength 400 nm is incident on a cesium plate at the rate of 5.0 W. The potential of the collector plate is made sufficiently positive with respect to the emitter, so that the current reaches its saturation value. Assuming that on average, one out of every 106 photons is able to eject a photoelectron, find the photocurrent in the circuit.
उत्तर
Given:-
Wavelength of light, λ = 400 nm
Power, P = 5 W
Energy of photon,
`E = (hc)/λ = (1242/400) "eV"`
Number of photons, n = `P/E`
`n = (5 xx 400)/(1.6 xx 10^-19 xx 1242)`
Number of electrons = 1 electron per 106 photons
Number of photoelectrons emitted,
`n' = (5 xx 400)/(1.6 xx 1242 xx 10^-19 xx 10^6)`
Photo electric current,
I = Number of electron `xx` Charge on electron
`I = (5 xx 400)/(1.6 xx 1242 xx 10^-19 xx 10^6) xx 1.6 xx 10^-19`
`= 1.6 xx 10^-6 "A" = 1.6 "uA"`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The threshold frequency for a certain metal is 3.3 × 1014 Hz. If light of frequency 8.2 × 1014 Hz is incident on the metal, predict the cutoff voltage for the photoelectric emission.
(a) A monoenergetic electron beam with electron speed of 5.20 × 106 m s−1 is subject to a magnetic field of 1.30 × 10−4 T normal to the beam velocity. What is the a radius of the circle traced by the beam, given e/m for electron equals 1.76 × 1011 C kg−1?
(b) Is the formula you employ in (a) valid for calculating the radius of the path of a 20 MeV electron beam? If not, in what way is it modified?
What is so special about the combination e/m? Why do we not simply talk of e and m separately?
If light of wavelength 412.5 nm is incident on each of the metals given below, which ones will show photoelectric emission and why?
| Metal | Work Function (eV) |
| Na | 1.92 |
| K | 2.15 |
| Ca | 3.20 |
| Mo | 4.17 |
Two neutral particles are kept 1 m apart. Suppose by some mechanism some charge is transferred from one particle to the other and the electric potential energy lost is completely converted into a photon. Calculate the longest and the next smaller wavelength of the photon possible.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A light beam of wavelength 400 nm is incident on a metal plate of work function 2.2 eV. (a) A particular electron absorbs a photon and makes two collisions before coming out of the metal. Assuming that 10% of the extra energy is lost to the metal in each collision, find the kinetic energy of this electron as it comes out of the metal. (b) Under the same assumptions, find the maximum number of collisions the electron can suffer before it becomes unable to come out of the metal.
A horizontal cesium plate (φ = 1.9 eV) is moved vertically downward at a constant speed v in a room full of radiation of wavelength 250 nm and above. What should be the minimum value of v so that the vertically-upward component of velocity is non-positive for each photoelectron?
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
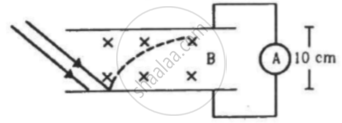
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, the emitter and the collector plates are placed at a separation of 10 cm and are connected through an ammeter without any cell. A magnetic field B exists parallel to the plates. The work function of the emitter is 2.39 eV and the light incident on it has wavelengths between 400 nm and 600 nm. Find the minimum value of B for which the current registered by the ammeter is zero. Neglect any effect of space charge.
A silver ball of radius 4.8 cm is suspended by a thread in a vacuum chamber. Ultraviolet light of wavelength 200 nm is incident on the ball for some time during which light energy of 1.0 × 10−7 J falls on the surface. Assuming that on average, one photon out of every ten thousand is able to eject a photoelectron, find the electric potential at the surface of the ball, assuming zero potential at infinity. What is the potential at the centre of the ball?
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Plot a graph to show the variation of stopping potential with frequency of incident radiation in relation to photoelectric effect.
The stopping potential in an experiment on photoelectric effect is 1.5V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted? Calculate in Joules.
Answer the following question.
Why is the wave theory of electromagnetic radiation not able to explain the photoelectric effect? How does a photon picture resolve this problem?
In the case of a photo electric effect experiment, explain the following facts, giving reasons.
The wave theory of light could not explain the existence of the threshold frequency.
In the experimental set up for studying photoelectric effect, if keeping the frequency of the incident radiation and the accelerating potential fixed, the intensity of light is varied, then ______.
When a beam of 10.6 eV photons of intensity 2.0 W/m2 falls on a platinum surface of area 1.0 × 10-4 m2, only 53% of the incident photons eject photoelectrons. The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is ______.
Cathode rays can be deflected by
In photoelectric effect, the photoelectric current
