Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Predict the major product of acid catalysed dehydration of butan-1-ol.
उत्तर
Acid catalysed dehydration of butan-1-ol produces but-2-ene as the main product and butan-1-ene as the secondary product. This is because dehydration of alcohols takes place through carbocation intermediates. Again, butan-1-ol being a 1° alcohol, on protonation and elimination of H2O, first gives a 1° carbocation (I), which being less stable rearranges to form more stable 2° carbocation (II), then it removes a proton in two different ways to form butan-2-ene or butan-1-ene. Since butan-2-ene is more stable, it is the main product according to Setzeff rule.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the reagents used in the following reactions:
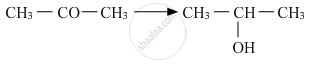
Predict the major product of acid catalysed dehydration of 1-methylcyclohexanol.
Write the mechanism of hydration of ethene to yield ethanol.
How is the following conversion carried out?
\[\ce{Ethyl magnesium chloride -> Propan-1-ol}\]
How is the following conversion carried out?
\[\ce{Methyl magnesium bromide → 2-Methylpropan-2-ol}\]
Name the reagent used in the following reaction:
Dehydration of propan-2-ol to propene.
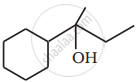
Show how you would synthesise the following alcohol from an appropriate alkene?
Write the structure of main compounds A and B in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2CN->[CH3MgBRH/3O+]A->[LiAIH4]B}\]
Primary alcohols are prepared by the reduction of carboxylic acids. Though lithium aluminium hydride is a strong reducing agent, it is not used in the reaction. This is so because:
Monochlorination of toluene in sunlight followed by hydrolysis by aq. \[\ce{NaOH}\] yields.
Why is the reactivity of all the three classes of alcohols with conc. \[\ce{HCl}\] and \[\ce{ZnCl2}\] (Lucas reagent) different?
Explain a process in which a biocatalyst is used in industrial preparation of a compound known to you.
Magnesium wire continues to burn in the atmosphere of CO2 because
Alkaline hydrolysis of an alkyl halide can be preferably carried out using ______.
The major product of acid catalysed dehydration of 1-methylcyclohexanol is ______.
An aldehyde isomeric with allyl alcohol gives phenyl hydrazone. Pick out a ketone that too gives a phenyl hydrazone containing the same percentage of nitrogen.
\[\ce{C3H8O ->[{[O]}][K2Cr2O7/H2SO4] C3H6O ->[I2 + NaOH(aq.)] CHI3}\]
In this reaction the first compound is:
\[\ce{? ->[\Delta, CN-][EtOH, H2O]}\] Benzoin.
The reactant is obtained by dry distillation of the calcium salts of the following pairs:
The major product of the following reaction is:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{Cl}\phantom{.........................}\\
|\phantom{..........................}\\
\ce{CH3 - CH - CH3 ->[(i) Alc. KOH][(ii) HBr/peroxide (iii) aq. KOH]}
\end{array}\]
How are the following conversions carried out?
\[\ce{Methyl magnesium bromide ->2-Methylpropan-2-ol}\]
