Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the following.
A balloon is inflated with helium gas at room temperature of 25°C and at 1 bar pressure when its initial volume is 2.27L and allowed to rise in the air. As it rises in the air external pressure decreases and the volume of the gas increases till finally, it bursts when external pressure is 0.3bar. What is the limit at which the volume of the balloon can stay inflated?
उत्तर
Given:
P1 = Initial pressure = 1 bar
V1 = Initial volume = 2.27 L
P2 = Final pressure = 0.3 bar
To find: V2 = Final volume
Formula: P1V1 = P2V2 (at constant n and T)
Calculation:
According to Boyle’s law,
P1V1 = P2V2 (at constant n and T)
∴ V2 = `("P"_1"V"_1)/"P"_2=(1xx2.27)/0.3` = 7.566667 L ≈ 7.567 L
The balloon can stay inflated below the volume of 7.567 L.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What would be the mass of CO2 occupying a volume of 44 litres at 25°C and 750 mm pressure.
Give reason for the following:
Gases exert pressure in all directions.
Answer in one sentence.
A bubble of methane gas rises from the bottom of the North sea. What will happen to the size of the bubble as it rises to the surface?
Convert the following temperature from degree Celcius to kelvin.
−15° C
Convert the following pressure value into Pascals.
10 atmosphere
Convert the following pressure value into Pascals.
107000 Nm−2
Convert the following pressure value into Pascals.
1 atmosphere
Convert 0.124 torr to the standard atmosphere
Identify the gas laws from the following diagram.
| Diagram | Gas laws |
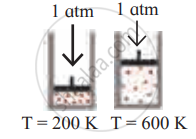 |
______________ |
Match the pairs of the following:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| a. Boyle’s law | i. at constant pressure and volume |
| b. Charles’ law | ii. at constant temperature |
| iii. at constant pressure |
Write the statement for Boyle’s law
The temperatures at which real gases obey the ideal gas laws over a wide range of pressure is called __________.
Give the mathematical expression that relates gas volume and moles.
Explain the following observation.
Liquid ammonia bottle is cooled before opening the seal
Of two samples of nitrogen gas, sample A contains 1.5 moles of nitrogen in a vessel of the volume of 37.6 dm3 at 298 K, and sample B is in a vessel of volume 16.5 dm3 at 298 K. Calculate the number of moles in sample B.
Sulphur hexafluoride is a colourless, odourless gas; calculate the pressure exerted by 1.82 moles of the gas in a steel vessel of volume 5.43 dm3 at 69.5 °C, assuming ideal gas behaviour
Hydrochloric acid is treated with a metal to produce hydrogen gas. Suppose a student carries out this reaction and collects a volume of 154.4 × 10−3 dm3 of a gas at a pressure of 742 mm of Hg at a temperature of 298 K. What mass of hydrogen gas (in mg) did the student collect?
At 25°C and 1 atm, a cylinder containing 10 L of an ideal gas is connected to the empty cylinder with a capacity of 20 L. The pressures exerted by gas m both the cylinders will be ____________.
A certain sample of gas has a volume of 0.2 L at one atmosphere pressure and 273.15 K. What is the volume of gas at 273.15°C at same pressure?
According to Andrews isothermals, the minimum temperature at which carbon dioxide gas obeys Boyles law is ______.
According to Andrews isothermals at what temperature the carbon dioxide gas starts to condense at 73 atmosphere?
At what temperature the volume of a gas becomes absolutely zero?
If 2 moles of an ideal gas at 546 K has volume of 44.8 L, then what will be it's pressure? (R = 0.082)
10 g of gas at one atomospheric pressure is cooled from 273.15°C to 0°C keeping the volume constant. What is the final pressure?
The number of molecules in 8.96 litres of gas at 0°C and 1 atm. pressure is approximately ______.
