Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State and explain Kirchhoff’s rules.
उत्तर
Kirchhoff’s first rule (current rule or junction rule):
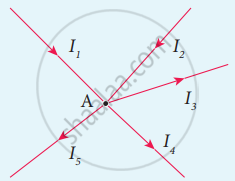
Statement: It states that the algebraic sum of the currents at any junction of a circuit is zero. It is a statement of conservation of electric charge.
Kirchhoff ’s current rule
Explanation:
All charges that enter a given junction in a circuit must leave that junction since charge cannot build up or disappear at a junction. Current entering the junction is taken as positive and current leaving the junction is taken as negative.
Applying this law to the junction A,
I1 + I2 – I3 – I4 – I5 = o
Or
I1 + I2 = + I3 I4 + I5
Kirchhoff’s second rule (voltage rule or loop rule):
Statement: It states that in a closed circuit the algebraic sum of the products of the current and resistance of each part of the circuit is equal to the total emf included in the circuit. This rule follows from the law of conservation of energy for an isolated system. (The energy supplied by the emf sources is equal to the sum of the energy delivered to all resistors).
Explanation:
The product of current and resistance is taken as positive when the direction of the current is followed. Suppose if the direction of current is opposite to the direction of the loop, then product of current and voltage across the resistor is negative. It is shown in following Fig. (a) and (b). The emf is considered positive when proceeding from the negative to the positive terminal of the cell. It is shown in following fig. (c) and (d).
(a)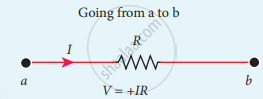
(b)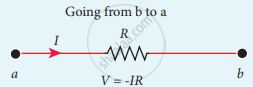
(c)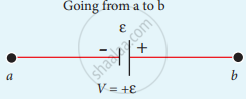
(d)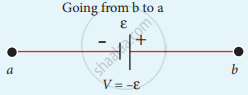
Kirchhoff voltage rule
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Kirchhoff's junction law is equivalent to .............................
(a) conservation of energy.
(b) conservation of charge
(c) conservation of electric potential
(d) conservation of electric flux
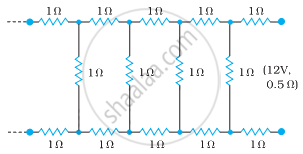
Determine the current drawn from a 12 V supply with internal resistance 0.5 Ω by the infinite network shown in the figure. Each resistor has 1 Ω resistance.
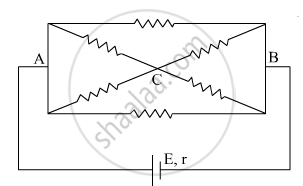
The current is drawn from a cell of emf E and internal resistance r connected to the network of resistors each of resistance r as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for
- the current draw from the cell and
- the power consumed in the network.
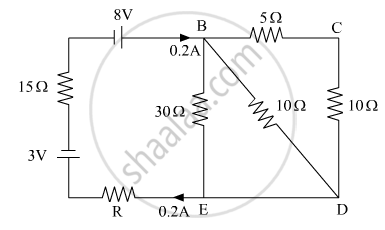
Calculate the value of the resistance R in the circuit shown in the figure so that the current in the circuit is 0.2 A. What would b the potential difference between points B and E?
In the given circuit, assuming point A to be at zero potential, use Kirchhoff’s rules to determine the potential at point B.

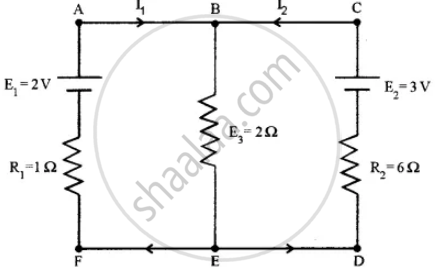
In the circuit shown in the figure below, E1 and E2 are two cells having emfs 2 V and 3 V respectively, and negligible internal resistance. Applying Kirchhoff’s laws of electrical networks, find the values of currents l1 and I2.
Solve the following question.
Using Kirchhoff’s rules, calculate the current through the 40 Ω and 20 Ω resistors in the following circuit.

State the principle of potentiometer.
How the emf of two cells are compared using potentiometer?
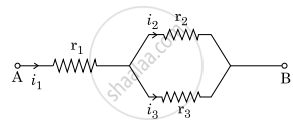
Three resistors having resistances r1, r2 and r3 are connected as shown in the given circuit. The ratio `"i"_3/"i"_1` of currents in terms of resistances used in the circuit is :