Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State and explain Pauli’s exclusion principle.
उत्तर
Pauli’s exclusion principle:
- Statement: “No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers”. OR “Only two electrons can occupy the same orbital and they must have opposite spins.”
- The capacity of an orbital to accommodate electrons is decided by Pauli’s exclusion principle.
- According to this principle, for an electron belonging to the same orbital, the spin quantum number must be different since the other three quantum numbers are the same.
- The spin quantum number can have two values: `+1/2` and `-1/2`.
- For example, consider helium (He) atom with electronic configuration 1s2.
For the two electrons in 1s orbital, the four quantum numbers are as follows:
Thus, in an atom, any two electrons can have the same three quantum numbers, but the fourth quantum number must be different.Electron number Quantum number Set of values of quantum numbers n l m s 1st Electron 1 0 0 `+1/2` `(1,0,0,+1/2)` 2nd Electron 1 0 0 `-1/2` `(1,0,0,-1/2)` - This leads to the conclusion that an orbital can accommodate a maximum of two electrons and if it has two electrons, they must have opposite spin.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Choose the correct option.
“No two electrons in the same atoms can have identical set of four quantum numbers”. This statement is known as -
State Heisenberg uncertainty principle.
Give the names of quantum numbers.
Define the term Electronic configuration
Write orbital notations for the electron in orbitals with the following quantum numbers.
n = 3, l = 2
Write condensed orbital notation of electronic configuration of the following element:
Lithium (Z = 3)
Write condensed orbital notation of electronic configuration of the following element:
Carbon (Z = 6)
Draw shapes of 2s orbitals.
Explain in brief, the significance of the azimuthal quantum number.
The principal quantum number (n) and magnetic quantum number (ml) for the valence electrons of rubidium atom (Z = 37) are ____________ respectively.
The designation of a subshell with n = 6 and l = 2 is ____________.
How many electrons can fit in the orbital for which n = 4 and l = 2?
Which one of the following is NOT possible?
The probability density plots of 1s and 2s orbitals are given in Figure:
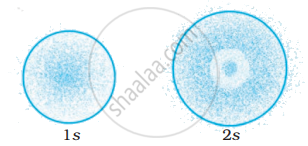
The density of dots in a region represents the probability density of finding electrons in the region.
On the basis of above diagram which of the following statements is incorrect?
Number of angular nodes for 4d orbital is ______.
Out of the following pairs of electrons, identify the pairs of electrons present in degenerate orbitals:
| (i) | (a) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = -2, m_s = - 1/2` |
| (b) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = -1, m_s = - 1/2` | |
| (ii) | (a) `n = 3, l = 1, m_l = 1, m_s = + 1/2` |
| (b) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = 1, m_s = + 1/2` | |
| (iii) | (a) `n = 4, l = 1, m_l = 1, m_s = + 1/2` |
| (b) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = 1, m_s = + 1/2` | |
| (iv) | (a) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = +2, m_s = - 1/2` |
| (b) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = +2, m_s = + 1/2` |
The arrangement of orbitals on the basis of energy is based upon their (n + l) value. Lower the value of (n + l), lower is the energy. For orbitals having same values of (n + l), the orbital with lower value of n will have lower energy.
Based upon the above information, arrange the following orbitals in the increasing order of energy.
1s, 2s, 3s, 2p
The arrangement of orbitals on the basis of energy is based upon their (n + l) value. Lower the value of (n + l), lower is the energy. For orbitals having same values of (n + l), the orbital with lower value of n will have lower energy.
Based upon the above information, solve the questions given below:
Which of the following orbitals has the lowest energy?
5p, 5d, 5f, 6s, 6p
Match the quantum numbers with the information provided by these.
| Quantum number | Information provided |
| (i) Principal quantum number | (a) orientation of the orbital |
| (ii) Azimuthal quantum number | (b) energy and size of orbital |
| (iii) Magnetic quantum number | (c) spin of electron |
| (iv) Spin quantum number | (d) shape of the orbital |
Match the following
| (i) Photon | (a) Value is 4 for N shell |
| (ii) Electron | (b) Probability density |
| (iii) ψ2 | (c) Always positive value |
| (iv) Principal quantum number n | (d) Exhibits both momentum and wavelength |
Match species given in Column I with the electronic configuration given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) \[\ce{Cr}\] | (a) [Ar]3d84s0 |
| (ii) \[\ce{Fe^{2+}}\] | (b) [Ar]3d104s1 |
| (iii) \[\ce{Ni^{2+}}\] | (c) [Ar]3d64s0 |
| (iv) \[\ce{Cu}\] | (d) [Ar] 3d54s1 |
| (e) [Ar]3d64s2 |
Which of the following is not the permissible arrangement of electrons in an atom?
In assigning R - S configuration, which among the following groups has highest priority?
In the case of R, S configuration the group having the highest priority is ______.
Which of the following element do not follow Aufbau principle?
Which one of the following laws will represent the pairing of electrons in a subshell after each orbital is filled with one electron?
