Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State Heisenberg uncertainty principle.
उत्तर
Heisenberg's uncertainty principle states that “It is impossible to determine simultaneously, the exact position and exact momentum (or velocity) of an electron”.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the term Electronic configuration
Explain the anomalous behaviour of copper.
Explain the anomalous behaviour of chromium.
Write orbital notations for the electron in orbitals with the following quantum numbers.
n = 2, l = 1
Write condensed orbital notation of electronic configuration of the following element:
Lithium (Z = 3)
Write condensed orbital notation of electronic configuration of the following element:
Oxygen (Z = 8)
Explain in brief, the significance of the azimuthal quantum number.
Using the concept of quantum numbers, calculate the maximum numbers of electrons present in the ‘M’ shell. Give their distribution in shells, subshells, and orbitals.
Indicate the number of unpaired electrons in \[\ce{Si}\] (Z = 14).
The designation of a subshell with n = 6 and l = 2 is ____________.
How many electrons in 19K have n = 3, l = 1?
The probability density plots of 1s and 2s orbitals are given in Figure:
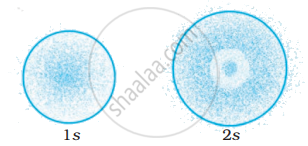
The density of dots in a region represents the probability density of finding electrons in the region.
On the basis of above diagram which of the following statements is incorrect?
Out of the following pairs of electrons, identify the pairs of electrons present in degenerate orbitals:
| (i) | (a) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = -2, m_s = - 1/2` |
| (b) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = -1, m_s = - 1/2` | |
| (ii) | (a) `n = 3, l = 1, m_l = 1, m_s = + 1/2` |
| (b) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = 1, m_s = + 1/2` | |
| (iii) | (a) `n = 4, l = 1, m_l = 1, m_s = + 1/2` |
| (b) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = 1, m_s = + 1/2` | |
| (iv) | (a) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = +2, m_s = - 1/2` |
| (b) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = +2, m_s = + 1/2` |
Which of the following sets of quantum numbers are correct?
| `n` | `l` | `m_l` | |
| (i) | 1 | 1 | +2 |
| (ii) | 2 | 1 | +1 |
| (iii) | 3 | 2 | –2 |
| (iv) | 3 | 4 | –2 |
In which of the following pairs, the ions are iso-electronic?
(i) \[\ce{Na^{+}, Mg^{2+}}\]
(ii) \[\ce{Al3^{+}, O-}\]
(iii) \[\ce{Na+ , O2-}\]
(iv) \[\ce{N3-, Cl-}\]
Which of the following statements concerning the quantum numbers are correct?
(i) Angular quantum number determines the three dimensional shape of the orbital.
(ii) The principal quantum number determines the orientation and energy of the orbital.
(iii) Magnetic quantum number determines the size of the orbital.
(iv) Spin quantum number of an electron determines the orientation of the spin of electron relative to the chosen axis.
Which of the following orbitals are degenerate?
3dxy, 4dxy 3dz2, 3dyz, 4dyz, 4dz2
Calculate the total number of angular nodes and radial nodes present in 3p orbital.
The arrangement of orbitals on the basis of energy is based upon their (n + l) value. Lower the value of (n + l), lower is the energy. For orbitals having same values of (n + l), the orbital with lower value of n will have lower energy.
Based upon the above information, arrange the following orbitals in the increasing order of energy.
1s, 2s, 3s, 2p
The arrangement of orbitals on the basis of energy is based upon their (n + l) value. Lower the value of (n + l), lower is the energy. For orbitals having same values of (n + l), the orbital with lower value of n will have lower energy.
Based upon the above information, arrange the following orbitals in the increasing order of energy.
4s, 3s, 3p, 4d
The arrangement of orbitals on the basis of energy is based upon their (n + l) value. Lower the value of (n + l), lower is the energy. For orbitals having same values of (n + l), the orbital with lower value of n will have lower energy.
Based upon the above information, arrange the following orbitals in the increasing order of energy.
5f, 6d, 7s, 7p
The arrangement of orbitals on the basis of energy is based upon their (n + l) value. Lower the value of (n + l), lower is the energy. For orbitals having same values of (n + l), the orbital with lower value of n will have lower energy.
Based upon the above information, solve the questions given below:
Which of the following orbitals has the lowest energy?
4d, 4f, 5s, 5p
The electronic configuration of valence shell of Cu is 3d104s1 and not 3d94s2. How is this configuration explained?
What is the difference between the terms orbit and orbital?
Match the following
| (i) Photon | (a) Value is 4 for N shell |
| (ii) Electron | (b) Probability density |
| (iii) ψ2 | (c) Always positive value |
| (iv) Principal quantum number n | (d) Exhibits both momentum and wavelength |
Choose the INCORRECT statement
In the case of R, S configuration the group having the highest priority is ______.
