Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State factors on which the amount of heat radiated by a body depends.
उत्तर
The amount of heat radiated by a body depends on:
- The absolute temperature of the body (T)
- The nature of the body – the material, nature of the surface - polished or not, etc.
- The surface area of the body (A)
- Time duration for which body emits radiation (t).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Given below are observations on molar specific heats at room temperature of some common gases.
| Gas |
Molar specific heat (Cv) (cal mol–1 K–1) |
| Hydrogen | 4.87 |
| Nitrogen | 4.97 |
| Oxygen | 5.02 |
| Nitric oxide | 4.99 |
| Carbon monoxide | 5.01 |
| Chlorine | 6.17 |
The measured molar specific heats of these gases are markedly different from those for monatomic gases. Typically, molar specific heat of a monatomic gas is 2.92 cal/mol K. Explain this difference. What can you infer from the somewhat larger (than the rest) value for chlorine?
You have a choice of three metals A, B, and C, of specific heat capacities 900 Jkg-1 °C-1, 380 Jkg-1 °C-1 and 460 Jkg-1 °C-1 respectively, to make a calorimeter. Which material will you select? Justify your answer.
A liquid X has the maximum specific heat capacity and is used as a coolant in Car Radiators. Name the liquid X.
The temperature of 170 g of water at 50°C is lowered to 5°C by adding a certain amount of ice to it. Find the mass of ice added.
Given: Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg-1 °C-1 and specific latent heat of ice = 336000 J kg-1.
State S.I. unit of specific heat capacity.
Water is used in hot water bottles for fomentation. Give a reason.
Give one example where high specific heat capacity of water is used as cooling purposes?
The specific heat capacity of water is :
Name the radiations for which the green house gases are transparent ?
The global warming has resulted:
(a) the increase in yield of crops
(b) the decrease in sea levels
(c) the decrease in human deaths
(d) the increase in sea levels
Solve the following problems:
Equal heat is given to two objects A and B of mass 1 g. Temperature of A increases by 3°C and B by 5°C. Which object has more specific heat? And by what factor?
Indian style of cooling drinking water is to keep it in a pitcher having porous walls. Water comes to the outer surface very slowly and evaporates. Most of energy needed for evaporation is taken from the water itself and the water is cooled down. Assume that a pitcher contains 10 kg of water and 0.2 g of water comes out per second. Assuming no backward heat transfer from the atmosphere to the water, calculate the time in which the temperature decrease by 5°C. Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg−1 °C−1 and latent heat of vaporization of water = 2.27 × 106 J kg−1.
650 J of heat is required to raise the temp. of 0.25 kg of lead from 15°C to 35°C. Calculate the Sp. heat capacity of lead.
Specific heat capacity of substance A is 3.8 J g-1 K-1whereas the specific heat capacity of substance B is 0.4 J g-1 K-1. Which of the two is a good conductor of heat? How is one led to this conclusion?
Write an expression for the heat energy liberated by a hot body.
Describe a method to determine the specific heat capacity of a solid (say, a piece of copper).
Discuss how high specific heat capacity of water helps in formation of land and sea breeze.
Solve the following problem.
Specific latent heat of vaporization of water is 2.26 × 106 J/kg. Calculate the energy needed to change 5.0 g of water into steam at 100 ºC.
Write a short note.
Specific heat capacity
For a gas, `"R"/"C"_"v"=0.4`, where R Is universal gas constant and Cv is the molar specific heat at constant volume. The gas is made up of molecules, which are ______
50 g of copper is heated to increase its temperature by 10° C. If the same quantity of heat is given to 5 g water, the rise in its temperature is [Specific heat of copper = 420 joule-kg-1 °C-1 , specific heat of water = 4200 joule-kg-I °C-1]
Which of the following substances (A, B and C) has the highest specific beat?
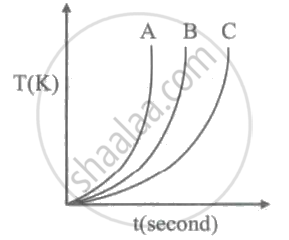
Which of the substances P, Q, or R has the lowest specific heat? The temperature v/s time graph is shown ______.

The molar specific heat of an ideal gas at constant pressure and constant volume is 'Cp' and 'Cv' respectively. If 'R' is the universal gas constant and the ratio 'Cp' to 'Cv' is 'γ' then CV = ______.
Specific heat capacity C = ______.
Find the odd one out:
Prove the Mayer's relation `C_p - C _v = R/J`
Calculate the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 200 g of copper from 20°C to 70°C. Specific heat capacity of copper = 390 J kg-1 K-1.
