Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The capacitance between the adjacent plates shown in the figure is 50 nF. A charge of 1.0µC is placed on the middle plate. If 1.0 µC is placed on the upper plate instead of the middle, what will be the potential difference between (a) the upper and the middle plates and (b) the middle and the lower plates?

उत्तर
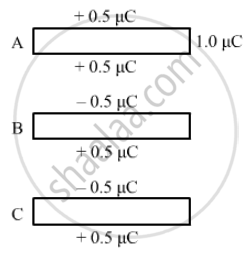
When 1µC charge is given to the upper plate, the charge gets distributed. The two sides of the upper plate have `+0.5 muC` charge. One side of the middle plate facing the upper plate has `-0.5 muC` charge and the other side has `+0.5 muC` Change . Similarly, one side of the lower plate facing the middle plate has `-0.5 muC` charge and the other side has `+0.5 muC` charge.
(a) Effective charge on the capacitor formed by the upper and middle plates = 0.5 µC
Capacitance = 50 nF = 0.05 µF
∴ Potential difference between the plates , `V = Q/C = (0.5 muC)/(0.05 muF) = 10 "V"`
(b) Effective charge on the capacitor formed by the middle and lower plates = 0.5 µC
Capacitance = 0.50 µF
∴ Potential difference between the plates, `V = Q/C = (0.5 muC)/(0.05 muF) = 10 "V"`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Distinguish between Conductors and Insulators.
The potential difference applied across a given resistor is altered so that the heat produced per second increases by a factor of 9. By what factor does the applied potential difference change?
A metal rod of square cross-sectional area A having length l has current I flowing through it when a potential difference of V volt is applied across its ends (figure I). Now the rod is cut parallel to its length into two identical pieces and joined as shown in figure II. What potential difference must be maintained across the length of 2l. so that the current in the rod is still I?

Explain the principle of a device that can build up high voltages of the order of a few million volts.
Draw a schematic diagram and explain the working of Van de Graff generator device.
A 100 pF capacitor is charged to a potential difference of 24 V. It is connected to an uncharged capacitor of capacitance 20 pF. What will be the new potential difference across the 100 pF capacitor?
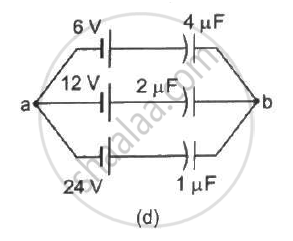
Find the potential difference `V_a - V_b` between the points a and b shown in each part of the figure.
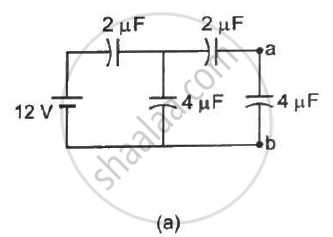
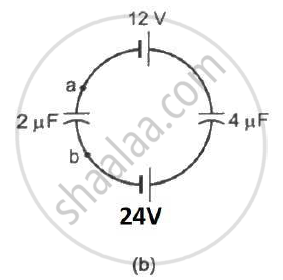
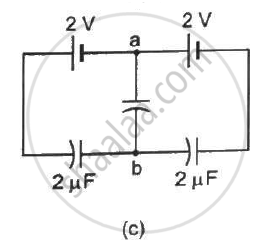
A charge of 1 µC is given to one plate of a parallel-plate capacitor of capacitance 0⋅1 µF and a charge of 2 µC is given to the other plate. Find the potential difference developed between the plates.
Two capacitors of capacitance 20⋅0 pF and 50⋅0 pF are connected in series with a 6⋅00 V battery. Find (a) the potential difference across each capacitor and (b) the energy stored in each capacitor.
A capacitor having a capacitance of 100 µF is charged to a potential difference of 50 V. (a) What is the magnitude of the charge on each plate? (b) The charging battery is disconnected and a dielectric of dielectric constant 2⋅5 is inserted. Calculate the new potential difference between the plates. (c) What charge would have produced this potential difference in absence of the dielectric slab. (d) Find the charge induced at a surface of the dielectric slab.
In circuits, a difference in potential from one point to another is often called ______.
If a positive charge moves in the direction of the electric field ______.
Assertion: Electric potential and electric potential energy are different quantities.
Reason: For a system of positive test charge and point charge electric potential energy = electric potential.
An α-particle and a proton are accelerate at same potential difference from rest. What will be the ratio of their final velocity?
On moving a charge of 20 C by 2 cm, 2 j of work is done then the potential difference between the point is:-
A bullet of mass of 2 g is having a charge of 2 µc. Through what potential difference must it be accelerated, starting from rest, to acquire a speed of 10 m/s.
If potential difference between the two ends of a metallic wire is doubled, drift speed of free electrons in the wire ______.
