Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The centre of mass of a system of particles is at the origin. It follows that
पर्याय
the number of particles to the right of the origin is equal to the number of particles to the left
the total mass of the particles to the right of the origin is same as the total mass to the left of the origin
the number of particles on X-axis should be equal to the number of particles on Y-axis
if there is a particle on the positive X-axis, there must be at least one particle on the negative X-axis
none of these
उत्तर
None .
The centre of mass of a system of particles depends on the product of individual masses and their distances from the origin.
Therefore, we may say about the given statements:
(a) Distance of particles from origin is not known.
(b) Masses are same but the distance of particles from the origin is not given.
(c) Distance of particles from origin is not given.
(d) It is not necessary that least one particle lies on the negative X-axis. The particles can be above the negative X-axis on X-Y plane.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give the location of the centre of mass of a
- sphere,
- cylinder,
- ring, and
- cube,
each of uniform mass density. Does the centre of mass of a body necessarily lie inside the body?
You are waiting for a train on a railway platform. Your three-year-old niece is standing on your iron trunk containing the luggage. Why does the trunk not recoil as she jumps off on the platform?
A circular plate of diameter d is kept in contact with a square plate of edge d as show in figure. The density of the material and the thickness are same everywhere. The centre of mass of the composite system will be 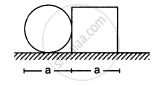
Consider a system of two identical particles. One of the particles is at rest and the other has an acceleration a. The centre of mass has an Acceleration
A nonzero external force acts on a system of particles. The velocity and the acceleration of the centre of mass are found to be v0 and a0 at instant t. It is possible that
(a) v0 = 0, a0 = 0
(b) v0 = 0, a0 ≠ 0
(c) v0 ≠ 0, a0 = 0
(d) v0 ≠ 0, a0 ≠ 0
A ball of mass m is dropped onto a floor from a certain height. The collision is perfectly elastic and the ball rebounds to the same height and again falls. Find the average force exerted by the ball on the floor during a long time interval.
In an elastic collision
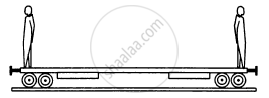
Two persons each of mass m are standing at the two extremes of a railroad car of mass M resting on a smooth track(In the following figure). The person on left jumps to the left with a horizontal speed u with respect to the state of the car before the jump. Thereafter, the other person jumps to the right, again with the same horizontal speed u with respect to the state of the car before his jump. Find the velocity of the car after both the persons have jumped off.
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Suppose each of the blocks is pulled by a constant force F instead of any impulse. Find the maximum elongation that the spring will suffer and the distance moved by the two blocks in the process.
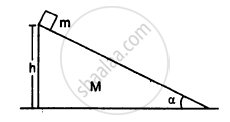
A block of mass m is placed on a triangular block of mass M which in turn is placed on a horizontal surface as shown in figure. Assuming frictionless surfaces find the velocity of the triangular block when the smaller block reaches the bottom end.
Two small balls A and B, each of mass m, are joined rigidly to the ends of a light rod of length L (see the following figure). The system translates on a frictionless horizontal surface with a velocity \[\nu_0\] in a direction perpendicular to the rod. A particle P of mass m kept at rest on the surface sticks to the ball A as the ball collides with it. Find
(a) the linear speeds of the balls A and B after the collision, (b) the velocity of the centre of mass C of the system A + B + P and (c) the angular speed of the system about C after the collision.
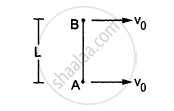
[Hint : The light rod will exert a force on the ball B
only along its length.]
The centre of mass of a system of particles does not depend upon, ______
The speed of the centre of a wheel rolling on a horizontal surface is vo. A point on the rim is level with the centre will be moving at a speed of, ______
Two particles P and Q of mass 1 kg and 3 kg respectively start moving towards each other from rest under mutual attraction. What is the velocity of their center of mass?
In system of two particles of masses 'm1' and 'm2', the first particle is moved by a distance 'd' towards the centre of mass. To keep the centre of mass unchanged, the second particle will have to be moved by a distance ______.
Three equal masses each of 50 g, are placed at the corners of a right angled isosceles triangle whose two equal sides are 5 cm each. The position of the centre of mass of the system is ____________.
A bullet of mass 20 gram is fired from a gun of mass 2.5 kg with a speed of 750 m/s. The magnitude of recoil velocity of the gun is ______.
The ratio of weights of a man inside a lift when it is stationary and when it is going down with a uniform acceleration 'a' is 3 : 2. The value of 'a' will be ______.
(a< g, g = acceleration due to gravity)
A uniform square plate has a small piece Q of an irregular shape removed and glued to the centre of the plate leaving a hole behind figure. The CM of the plate is now in the following quadrant of x-y plane ______.
