Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The difference in the frequencies of series limit of Lyman series and Balmer series is equal to the frequency of the first line of the Lyman series. Explain.
उत्तर
The 'series limit' refers to the 'shortest wavelength' (corresponding to the maximum photon energy).
The frequency of the radiation emitted for transition from n1 to n2 is given by
`f = k (1/n_1^2 - 1/n_2^2)`
Here, k is a constant.
For the series limit of Lyman series,
`n_1 = 1`
`n_2 = ∞`
Frequency, `f_1 = k( 1/1^2 - 1/∞ ) = k`
For the first line of Lyman series,
`n_1 = 1`
`n_2 = 2`
Frequency, `f_2 = k(1/1^2 - 1/2^2) = (3k)/4`
For series limit of Balmer series,
`n_1 = 2`
`n_2 = ∞ `
`f_1 = k(1/2^2 - 1 /∞) = k/4`
`f_1 - f_3 = f_2`
Thus, the difference in the frequencies of series limit of Lyman series and Balmer series is equal to the frequency of the first line of the Lyman series.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Bohr’s third postulate for hydrogen (H2) atom. Derive Bohr’s formula for the wave number. Obtain expressions for longest and shortest wavelength of spectral lines in ultraviolet region for hydrogen atom
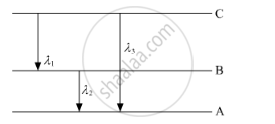
(i) State Bohr's quantization condition for defining stationary orbits. How does the de Broglie hypothesis explain the stationary orbits?
(ii) Find the relation between three wavelengths λ1, λ2 and λ3 from the energy-level diagram shown below.
Using Bohr's postulates, derive the expression for the orbital period of the electron moving in the nth orbit of hydrogen atom ?
The numerical value of ionization energy in eV equals the ionization potential in volts. Does the equality hold if these quantities are measured in some other units?
According to Maxwell's theory of electrodynamics, an electron going in a circle should emit radiation of frequency equal to its frequency of revolution. What should be the wavelength of the radiation emitted by a hydrogen atom in ground state if this rule is followed?
Consider a neutron and an electron bound to each other due to gravitational force. Assuming Bohr's quantization rule for angular momentum to be valid in this case, derive an expression for the energy of the neutron-electron system.
According to Bohr, 'Angular momentum of an orbiting electron is quantized'. What is meant by this statement?
Draw energy level diagram for a hydrogen atom, showing the first four energy levels corresponding to n=1, 2, 3 and 4. Show transitions responsible for:
(i) Absorption spectrum of Lyman series.
(ii) The emission spectrum of the Balmer series.
The dissociation constant of a weak base (BOH) is 1.8 × 10−5. Its degree of dissociation in 0.001 M solution is ____________.
A particle has a mass of 0.002 kg and uncertainty in its velocity is 9.2 × 10−6 m/s, then uncertainty in position is ≥ ____________.
(h = 6.6 × 10−34 J s)
According to Bohr’s theory, the angular momentum of an electron in 5th orbit is ______.
Why was a change in the Bohr Model of atom required? Due to which important development (s), concept of movement of an electron in an orbit was replaced by, the concept of probability of finding electron in an orbital? What is the name given to the changed model of atom?
Consider two different hydrogen atoms. The electron in each atom is in an excited state. Is it possible for the electrons to have different energies but same orbital angular momentum according to the Bohr model? Justify your answer.
According to the Bohr theory of H-atom, the speed of the electron, its energy and the radius of its orbit varies with the principal quantum number n, respectively, as:
The inverse square law in electrostatics is |F| = `e^2/((4πε_0).r^2)` for the force between an electron and a proton. The `(1/r)` dependence of |F| can be understood in quantum theory as being due to the fact that the ‘particle’ of light (photon) is massless. If photons had a mass mp, force would be modified to |F| = `e^2/((4πε_0)r^2) [1/r^2 + λ/r]`, exp (– λr) where λ = mpc/h and h = `h/(2π)`. Estimate the change in the ground state energy of a H-atom if mp were 10-6 times the mass of an electron.
The value of angular momentum for He+ ion in the first Bohr orbit is ______.
The first ionization energy of H is 21.79 × 10-19 J. The second ionization energy of He atom is ______ × 10-19J.
What is the energy associated with first orbit of Li2+ (RH = 2.18 × 10-18)?
In hydrogen atom, transition from the state n = 6 to n = 1 results in ultraviolet radiation. Infrared radiation will be obtained in the transition ______.
Write the ionisation energy value for the hydrogen atom.
