Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The displacement of a string is given by y (x, t) = 0.06 sin (2πx/3) cos (120 πt) where x and y are in m and t in s. The length of the string is 1.5 m and its mass is 3.0 × 10−2 kg.
- It represents a progressive wave of frequency 60 Hz.
- It represents a stationary wave of frequency 60 Hz.
- It is the result of superposition of two waves of wavelength 3 m, frequency 60 Hz each travelling with a speed of 180 m/s in opposite direction.
- Amplitude of this wave is constant.
उत्तर
b and c
Explanation:
We know that the standard equation of stationary wave is `y(x, t) = a sin(kx) cos(ωt)`
Given equation is `y(x, t) = 0.06 sin((2πx)/3) cos(120 πt)`
a. Comparing with a standard equation of stationary wave `y(x, t) = a sin(kx) cos(ωt)` Clearly, the given equation belongs to stationary wave. Hence, option (a) is not correct.
b. By comparing,
ω = 120 π
⇒ 2πf = 120 π
⇒ f = 60 Hz
c. k = `(2π)/3 = (2π)/λ`
⇒ λ = wavelength = 3m
Frequency = f = 60 Hz
Speed = v = fλ = (60 Hz) (3m) = 180 m/s
d. Since in stationary waves, all particles of the medium execute SHM with varying amplitude nodes.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A pipe 20 cm long is closed at one end. Which harmonic mode of the pipe is resonantly excited by a 430 Hz source? Will the same source be in resonance with the pipe if both ends are open? (Speed of sound in air is 340 m s–1).
Explain why (or how) In a sound wave, a displacement node is a pressure antinode and vice versa,
Two wires are kept tight between the same pair of supports. The tensions in the wires are in the ratio 2 : 1 the radii are in the ratio 3 : 1 and the densities are in the ratio 1 : 2. Find the ratio of their fundamental frequencies.
Water waves produced by a motor boat sailing in water are ______.
A sonometer wire is vibrating in resonance with a tuning fork. Keeping the tension applied same, the length of the wire is doubled. Under what conditions would the tuning fork still be is resonance with the wire?
The pattern of standing waves formed on a stretched string at two instants of time are shown in figure. The velocity of two waves superimposing to form stationary waves is 360 ms–1 and their frequencies are 256 Hz.

- Calculate the time at which the second curve is plotted.
- Mark nodes and antinodes on the curve.
- Calculate the distance between A′ and C′.
Show that when a string fixed at its two ends vibrates in 1 loop, 2 loops, 3 loops and 4 loops, the frequencies are in the ratio 1:2:3:4.
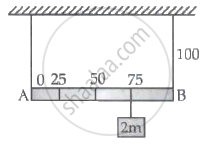
Shown in the figure is rigid and uniform one meter long rod AB held in horizontal position by two strings tied to its ends and attached to the ceiling. The rod is of mass 'm' and has another weight of mass 2m hung at a distance of 75 cm from A. The tension in the string at A is :
A tuning fork of frequency 480 Hz is used in an experiment for measuring the speed of sound (ν) in the air by resonance tube method. Resonance is observed to occur at two successive lengths of the air column, l1 = 30 cm and l2 = 70 cm. Then, ν is equal to ______.
A string 2.0 m long and fixed at its ends is driven by a 240 Hz vibrator. The string vibrates in its third harmonic mode. The speed of the wave and its fundamental frequency is ______.
