Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The displacement of a string is given by y (x, t) = 0.06 sin (2πx/3) cos (120 πt) where x and y are in m and t in s. The length of the string is 1.5 m and its mass is 3.0 × 10−2 kg.
- It represents a progressive wave of frequency 60 Hz.
- It represents a stationary wave of frequency 60 Hz.
- It is the result of superposition of two waves of wavelength 3 m, frequency 60 Hz each travelling with a speed of 180 m/s in opposite direction.
- Amplitude of this wave is constant.
Solution
b and c
Explanation:
We know that the standard equation of stationary wave is `y(x, t) = a sin(kx) cos(ωt)`
Given equation is `y(x, t) = 0.06 sin((2πx)/3) cos(120 πt)`
a. Comparing with a standard equation of stationary wave `y(x, t) = a sin(kx) cos(ωt)` Clearly, the given equation belongs to stationary wave. Hence, option (a) is not correct.
b. By comparing,
ω = 120 π
⇒ 2πf = 120 π
⇒ f = 60 Hz
c. k = `(2π)/3 = (2π)/λ`
⇒ λ = wavelength = 3m
Frequency = f = 60 Hz
Speed = v = fλ = (60 Hz) (3m) = 180 m/s
d. Since in stationary waves, all particles of the medium execute SHM with varying amplitude nodes.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A bat is flitting about in a cave, navigating via ultrasonic beeps. Assume that the sound emission frequency of the bat is 40 kHz. During one fast swoop directly toward a flat wall surface, the bat is moving at 0.03 times the speed of sound in air. What frequency does the bat hear reflected off the wall?
A 2 m long string fixed at both ends is set into vibrations in its first overtone. The wave speed on the string is 200 m s−1 and the amplitude is 0⋅5 cm. (a) Find the wavelength and the frequency. (b) Write the equation giving the displacement of different points as a function of time. Choose the X-axis along the string with the origin at one end and t = 0 at the instant when the point x = 50 cm has reached its maximum displacement.
Two wires of same material are vibrating under the same tension. If the first overtone of first wire is equal to the second overtone of second wire and radius of first wire is twice the radius of the second then the ratio of length of first wire to second wire is
The number of possible natural oscillations of the air column in a pipe closed at one end of length 85 cm whose frequencies lie below 1250 Hz? (v = 340 m/s)
Water waves produced by a motor boat sailing in water are ______.
The transverse displacement of a string (clamped at its both ends) is given by y(x, t) = 0.06 sin (2πx/3) cos (120 πt). All the points on the string between two consecutive nodes vibrate with ______.
- same frequency
- same phase
- same energy
- different amplitude.
Which of the following statements are true for a stationary wave?
- Every particle has a fixed amplitude which is different from the amplitude of its nearest particle.
- All the particles cross their mean position at the same time.
- All the particles are oscillating with same amplitude.
- There is no net transfer of energy across any plane.
- There are some particles which are always at rest.
Show that when a string fixed at its two ends vibrates in 1 loop, 2 loops, 3 loops and 4 loops, the frequencies are in the ratio 1:2:3:4.
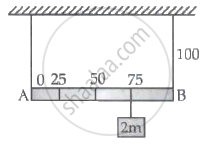
Shown in the figure is rigid and uniform one meter long rod AB held in horizontal position by two strings tied to its ends and attached to the ceiling. The rod is of mass 'm' and has another weight of mass 2m hung at a distance of 75 cm from A. The tension in the string at A is :
A tuning fork of frequency 480 Hz is used in an experiment for measuring the speed of sound (ν) in the air by resonance tube method. Resonance is observed to occur at two successive lengths of the air column, l1 = 30 cm and l2 = 70 cm. Then, ν is equal to ______.
