Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
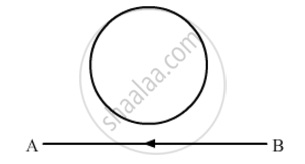
The electric current flowing in a wire in the direction from B to A is decreasing. Find out the direction of the induced current in the metallic loop kept above the wire as shown.
उत्तर
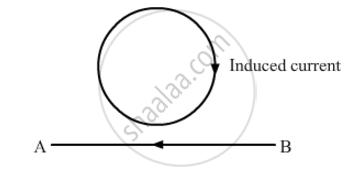
The decreasing magnetic field in the loop due to the decreasing current in wire AB is into the plane of the paper (perpendicular to the plane). So, the direction of the induced current in the loop will be such that it produces an inward magnetic field (perpendicular to the plane). Thus, the current induced in the loop is in clockwise direction (using the right-hand thumb rule)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Seema’s uncle was advised by his doctor to have an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan of his brain. Her uncle felt it to be expensive and wanted to postpone it. When Seema learnt about this, she took the help of her family and also approached the doctor, who also offered a substantial discount. She then convinced her uncle to undergo the test to enable the doctor to know the condition of his brain. The information thus obtained greatly helped the doctor to treat him properly.
Based on the above paragraph, answer the following questions:
(a) What according to you are the values displayed by Seema, her family and the doctor?
(b) What could be the possible reason for MRI test to be so expensive?
(c) Assuming that MRI test was performed using a magnetic field of 0.1 T, find the minimum and maximum values of the force that the magnetic field could exert on a proton (charge = 1.6 x 10-19 C) moving with a speed of 104 m/s.
Deduce the expression for the magnetic field at a point on the axis of a current carrying circular loop of radius ‘R’ distant ‘x’ from the centre. Hence, write the magnetic field at the centre of a loop.
A circular coil carrying a current I has radius R and number of turns N. If all the three, i.e. the current
I, radius R and number of turns N are doubled, then, the magnetic field at its centre becomes:
(a) Double
(b) Half
(c) Four times
(d) One fourth
A particle of charge ‘q’ and mass ‘m’ is moving with velocity .`vecV` It is subjected to a uniform magnetic field `vecB` directed perpendicular to its velocity. Show that it describes a circular path. Write the expression for its radius.
A circular current loop of magnetic moment M is in an arbitrary orientation in an external magnetic field B. The work done to rotate the loop by 30° about an axis perpendicular to its plane is ______.
An electron enters with a velocity v = v0i into a cubical region (faces parallel to coordinate planes) in which there are uniform electric and magnetic fields. The orbit of the electron is found to spiral down inside the cube in plane parallel to the x-y plane. Suggest a configuration of fields E and B that can lead to it.
The unit Wbm-2 is equal to ______.
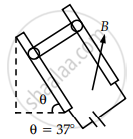
Two conducting rails are connected to a source of emf and form an incline as shown in figure. A bar of mass 50 g slides without friction down the incline through a vertical magnetic field B. If the length of the bar is 50 cm and a current of 2.5 A is provided by battery. Value of B for which the bar slide at a constant velocity ______ × 10-1 Tesla. 2 [g = 10 m/s2]
State dimensions of magnetic field.
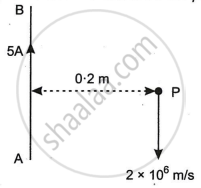
A long straight wire AB carries a current of 5A. P is a proton travelling with a velocity of 2 × 106 m/s, parallel to the wire, 0.2 m from it and in a direction opposite to the current, as shown in Figure below. Calculate the force which magnetic field of the current carrying conductor AB exerts on the proton.