Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The following table gives the distribution of IQ's (intelligence quotients) of 60 pupils of class V in a school:
| IQ's: | 125.5 to 13.25 |
118.5 to 125.5 |
111.5 to 118.5 |
104.5 to 111.5 |
97.5 to 104.5 |
90.5 to 97.5 |
83.5 to 90.5 |
76.5 to 83.5 |
69.5 to 76.5 |
62.5 to 69.5 |
| No. of pupils: |
1 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 5 | 3 | 1 |
Draw a frequency polygon for the above data.
उत्तर १
We first draw horizontal and vertical axes. Let us consider that the horizontal and vertical axes represent the class-limits and the frequencies of the class-intervals respectively.
The given data is a continuous grouped frequency distribution with equal class-intervals. To draw the frequency polygon of the given data without using histogram, obtain the class-limits of the class intervals. Obtain the class-limits of two class-intervals of 0 frequencies, i.e. on the horizontal axis, one adjacent to the first, on its left and one adjacent to the last, on its right. These class-intervals are known as imagined class-intervals. Then plot the frequencies against class-limits.
The following table is useful to draw the frequency polygon of the given data.
| Class - Intervals | Class - Marks | Frequency |
| 55.5-62.5 | 59 | 0 |
| 62.5-69.5 | ||
We represent class marks on X-axis on a suitable scale and the frequencies on Y-axis on a suitable scale.
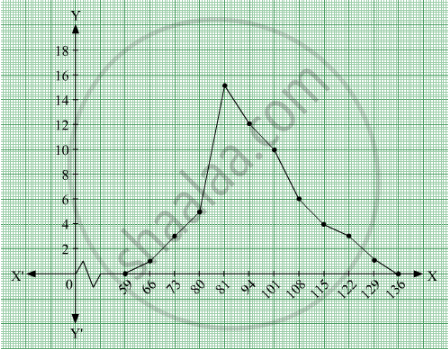
To obtain the frequency polygon we plot the points (66, 1), (73, 3), (80, 5), (87, 15), (94, 12), (101, 10), (108, 6), (115, 4), (122, 3), (129, 1).
Now we join the plotted points by line segments. The end points (66, 1) and (129, 1) are joined to the mid points (59, 0) and ( 136, 0) respectively of imagined class intervals to obtain the frequency polygon.
उत्तर २
We first draw horizontal and vertical axes. Let us consider that the horizontal and vertical axes represent the class-limits and the frequencies of the class-intervals respectively.
The given data is a continuous grouped frequency distribution with equal class-intervals. To draw the frequency polygon of the given data without using histogram, obtain the class-limits of the class intervals. Obtain the class-limits of two class-intervals of 0 frequencies, i.e. on the horizontal axis, one adjacent to the first, on its left and one adjacent to the last, on its right. These class-intervals are known as imagined class-intervals. Then plot the frequencies against class-limits.
The following table is useful to draw the frequency polygon of the given data.
| Class - Intervals | Class - Marks | Frequency |
| 55.5-62.5 | 59 | 0 |
| 62.5-69.5 | 66 | 1 |
| 69.5 - 76.5 | 73 | 3 |
| 76.5 - 83.5 | 80 | 5 |
| 83.5 - 90.5 | 87 | 15 |
| 90.5 - 97.5 | 94 | 12 |
| 97.5-104.5 | 101 | 10 |
| 104-111.5 | 108 | 6 |
| 111.5 - 118.5 | 115 | 4 |
| 118.5-125.5 | 122 | 3 |
| 125.5-132.5 | 129 | 1 |
| 132.5-139.5 | 136 | 0 |
We represent class marks on X-axis on a suitable scale and the frequencies on Y-axis on a suitable scale.
To obtain the frequency polygon we plot the points (66, 1), (73, 3), (80, 5), (87, 15), (94, 12), (101, 10), (108, 6), (115, 4), (122, 3), (129, 1).
Now we join the plotted points by line segments. The end points (66, 1) and (129, 1) are joined to the mid points (59, 0) and ( 136, 0) respectively of imagined class intervals to obtain the frequency polygon.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The following table gives the life times of 400 neon lamps:-
| Life time (in hours) | Number of lamps |
| 300 - 400 | 14 |
| 400 - 500 | 56 |
| 500 - 600 | 60 |
| 600 - 700 | 86 |
| 700 - 800 | 74 |
| 800 - 900 | 62 |
| 900 - 1000 | 48 |
- Represent the given information with the help of a histogram.
- How many lamps have a life time of more than 700 hours?
Read the bar graph given in Fig. 23.22 and answer the following questions:
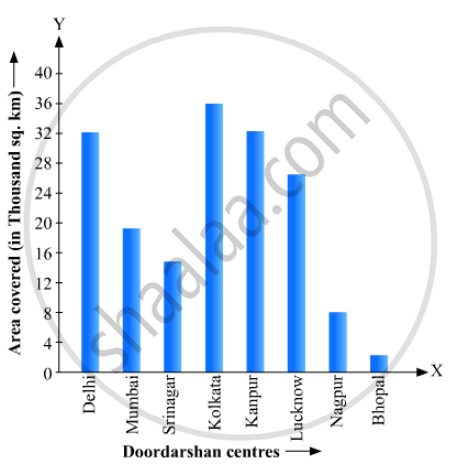
(i) What information is given by the bar graph?
(ii) Which Doordarshan centre covers maximum area? Also tell the covered area.
(iii) What is the difference between the areas covered by the centres at delhi and Bombay?
(iv) Which Doordarshan centres are in U.P State? What are the areas covered by them?
The following data shows the average age of men in various countries in a certain year:
| Country | India | Nepal | China | Pakistan | U.K | U.S.A |
| Average age (in years) |
55 | 52 | 60 | 50 | 70 | 75 |
Represent the above information by a bar graph.
The income and expenditure for 5 years of a family is given in the following data:
| Years | 1995-96 | 1996-97 | 1997-98 | 1998-99 | 1999-2000 |
| Income (Rs. inthousands) |
100 | 140 | 150 | 170 | 210 |
| Expenditure (Rs. in thousands) |
80 | 130 | 145 | 160 | 190 |
Represent the above data by a gar graph.
A frequency polygon is constructed by plotting frequency of the class interval and the
Students of a small school use different modes of travel to school as shown below:
| Mode | Bus | Car | Bicycle | Auto | On foot |
| No. of students | 142 | 98 | 50 | 34 | 16 |
Draw a suitable bar graph.
The frequency distribution has been represented graphically as follows:
| Marks | 0 – 20 | 20 – 40 | 40 – 60 | 60 – 100 |
| Number of Students | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 |
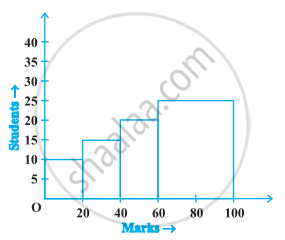
Do you think this representation is correct? Why?
The expenditure of a family on different heads in a month is given below:
| Head | Food | Education | Clothing | House Rent | Others | Savings |
| Expenditure (in Rs) |
4000 | 2500 | 1000 | 3500 | 2500 | 1500 |
Draw a bar graph to represent the data above.
The following table gives the frequencies of most commonly used letters a, e, i, o, r, t, u from a page of a book:
| Letters | a | e | i | o | r | t | u |
| Frequency | 75 | 125 | 80 | 70 | 80 | 95 | 75 |
Represent the information above by a bar graph.
Draw a histogram of the following distribution:
| Heights (in cm) | Number of students |
| 150 – 153 | 7 |
| 153 – 156 | 8 |
| 156 – 159 | 14 |
| 159 – 162 | 10 |
| 162 – 165 | 6 |
| 165 – 168 | 5 |
