Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The image obtained while finding the focal length of convex lens is ....................
पर्याय
a) a real and erect.
b) virtual and erect.
c) real and inverted.
d) virtual and inverted.
उत्तर
c) real and inverted.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student is using a convex lens of focal length 18 cm to study the image formation by it for the various positions of the object. He observes that when he places the object at 27 cm, the location of the image is at 54 cm on the other side of the lens. Identify from the following diagram the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used to draw the corresponding ray diagram.
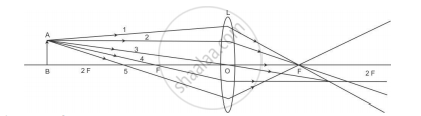
(A) 1, 2 and 4
(B) 1, 3 and 5
(C) 2, 4 and 5
(D) 2, 3 and 4
To determine the approximate focal length of the given convex lens by focussing a distant object (say, a sign board), you try to focus the image of the object on a screen. The image you obtain on the screen is always
(a) erect and laterally inverted
(b) erect and diminished
(c) inverted and diminished
(d) virtual, inverted and diminished
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on the walls of school laboratory by using a lens:-
(a) Which type of lens should be use and why?
(b) At what distance in terms of focal length 'F' of the lens should be place the candle flame so as to get (i) a magnified, and (ii) a diminished image respectively on the wall?
(c) Draw ray diagram to show the formation of the image in each case?
Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary?
An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens.
Write one condition where it does not bend when entering a medium of different optical density.
An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. Find :
1) the position of the image
2) nature of the image
A beam of light travelling in a rectangular glass slab emerges into air. Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light passes through a parallel sided glass block:
if it hits the glass block at 90° (that is, perpendicular to the glass block)
If an object is placed at the focus of a convex lens, where is the image formed?
State any two uses of convex lenses.
Distinguish between a convex lens and concave lens. Which of the two is a converging lens : convex lens of concave lens?
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed in front of a convex lens between focus and optical centre. State three characteristics of the image formed.
How could you find the focal length of a convex lens rapidly but approximately?
With the help of a labelled diagram explain how a convex lens converges a beam of parallel light rays. Mark the principal axis, optical centre, principal focus and focal length of the convex lens on the diagram.
Name one simple optical instrument in which the above arrangement of convex lens is used.
Describe the nature of image formed when an object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex lens of focal length 15 cm.
Calculate the focal length of a convex lens which produces a virtual image at a distance of 50 cm of an object placed 20 cm in front of it.
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.15 m
A convex lens of focal length 15 cm produces a magnification of +4. The object is placed:
(a) at a distance of 15 cm
(b) between 15 cm and 30 cm
(c) at less than 15 cm
(d) beyond 30 cm
What would be the diameter of the image of the flower on the film?
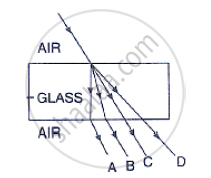
In figure , name the ray which represents the correct path of light while emerging out through
a glass block.
The given below figure shows an object OA and its image IB formed by a lens
. 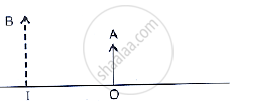
draw suitable rays to locate the lens and its focus.
A convex lens forms an image of an object equal to the size of the object. Draw a diagram to illustrate it.
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is upright and enlarged?
For which position of the object does a convex lens form a virtual and erect image? Explain with the help of a ray diagram.
Draw neat diagram to show the
Convergent action of a convex lens,
(a) What type of a lens can be used as a magnifying glass?
(b) Show by a ray diagram the formation of a real image by simple magnifying lens.
A convex lens forms an inverted image of size same as that of the object which is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of the lens. Find: The position of image
Answer the following question.
List four precautions which a student should observe while determining the focal length of a given convex lens by obtaining an image of a distant object on a screen.
What is the difference between a double convex and a bi-convex lens?
A candle is placed between f and 2f a convex lens. Draw a ray diagram showing the position of the image.
How will you determine the focal length of a convex lens by the plane mirror method?
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
A beam of light is incident through the holes on side A and emerges out of the holes on the other face of the box as show in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?
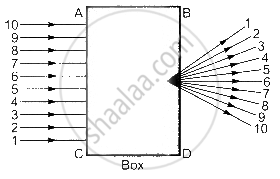
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex Lens.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
