Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The molar conductivity of 0.025 mol L−1 methanoic acid is 46.1 S cm2 mol−1. Calculate its degree of dissociation and dissociation constant. Given \[\ce{λ^0_{(H^+)}}\] = 349.6 S cm2 mol−1 and \[\ce{λ^0_{(HCOO^-)}}\] = 54.6 S cm2 mol−1.
उत्तर
\[\ce{∧^0_{{m}(HCOOH)} = λ^0_{(H^+)} + λ^0_{(HCOO^-)}}\]
= 349.6 + 54.6
= 404.2 S cm2 mol−1
Given: \[\ce{∧_{{m}(HCOOH)}}\] = 46.1 S cm2 mol−1
Degree of dissociation, α = `∧_"m"/(∧_"m"^0)`
= `(46.1 "S cm"^2 "mol"^-1)/(404.2 "S cm"^2 "mol"^-1)`
= 0.114
\[\ce{HCOOH ⇌ HCOO^- + H^+}\]
| Initial concentration | c mol L−1 | 0 | 0 |
| Concentration at equilibrium | c(1 − α) | cα | cα |
∴ Kα = `("c"α . "c"α)/("c"(1 - α))`
= `("c"α^2)/(1 - α)`
= `(0.025 xx (0.114)^2)/(1 - 0.114)`
= 3.67 × 10−4
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define "Molar conductivity".
The molar conductivity of cation and anion of salt BA are 180 and 220 mhos respectively. The molar conductivity of salt BA at infinite dilution is_____________ .
(a) 90 mhos.cm2
(b) 110 mhos.cm2.mol-1
(c) 200 mhos.cm2.mol-1
(d) 400 mhos.cm2.mol-1
Define limiting molar conductivity.
Why conductivity of an electrolyte solution decreases with the decrease in concentration ?
The conductivity of 0.20 mol L−1 solution of KCl is 2.48 × 10−2 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation (α). Given λ0 (K+) = 73.5 S cm2 mol−1 and λ0 (C1−) = 76.5 S cm2 mol−1.
State Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions.
Conductivity of 0.00241 M acetic acid is 7.896 × 10−5 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity and if `∧_"m"^0` for acetic acid is 390.5 S cm2 mol−1, what is its dissociation constant?
Define the following terms :
Limiting molar conductivity
How can you determine limiting molar conductivity, 0 m for strong electrolyte and weak electrolyte?
Conductivity always decreases with decrease in concentration both, for weak and strong electrolytes because of the fact that ____________.
Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions states ____________.
Which of the statements about solutions of electrolytes is not correct?
\[\ce{Λ^0_m}_{(NH_4OH)}\] is equal to ______.
Why on dilution the m Λm of \[\ce{CH3COOH}\] increases very fast, while that of \[\ce{CH3COONa}\] increases gradually?
Match the items of Column I and Column II on the basis of data given below:
`E_("F"_2//"F"^-)^Θ` = 2.87 V, `"E"_(("Li"^(+))//("Li"^-))^Θ` = − 3.5V, `"E"_(("Au"^(3+))//("Au"))^Θ` = 1.4 V, `"E"_(("Br"_(2))//("Br"^-))^Θ` = 1.09 V
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) F2 | (a) metal is the strongest reducing agent |
| (ii) Li | (b) metal ion which is the weakest oxidising agent |
| (iii) Au3+ | (c) non metal which is the best oxidising agent |
| (iv) Br– | (d) unreactive metal |
| (v) Au | (e) anion that can be oxidised by Au3+ |
| (vi) Li+ | (f) anion which is the weakest reducing agent |
| (vii) F– | (g) metal ion which is an oxidising agent |
Consider figure and answer the question to given below.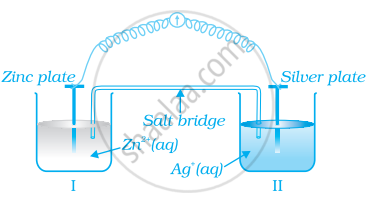
How will the concentration of Zn2+ ions and Ag+ ions be affected after the cell becomes ‘dead’?
The solubility of Co2[Fe(CN)6] in water at 25°C from the following data:
Conductivity of saturated solution of Co2[Fe(CN)6] = 2.06 × 10−6 ohm−1 cm−1 and that of water = 4.1 × 10−7 ohm−1 cm−1. The ionic molar conductivities of Co2+ and [Fe(CN)6]4− are 86 and 444 ohm−1 cm2 mol−1 respectively, is ______ × 10−6 mol/L.
The variation of molar conductivity with concentration of an electrolyte (X) m aqueous solution is shown in the given figure.
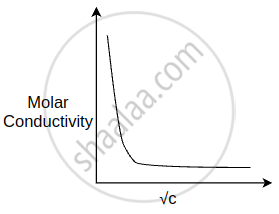
The electrolyte X is ______.
The unit of molar conductivity is ______.
The resistance of a conductivity cell with a 0.1 M KCl solution is 200 ohm. When the same cell is filled with a 0.02 M NaCl solution, the resistance is 1100 ohm. If the conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution is 0.0129 ohm-1 cm-1, calculate the cell constant and molar conductivity of 0.02 M NaCl solution.
