Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
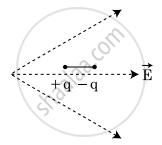
Two particles, carrying charges −q and +q and and of mass m each, are fixed at the ends of a light rod of length a to form a dipole. The rod is clamped at an end and is placed in a uniform electric field E with the axis of the dipole along the electric field. The rod is slightly tilted and then released. Neglecting gravity, find the time period of small oscillations.
उत्तर
Consider the rod to be a simple pendulum
Time period of a simple pendulum,
(where l = length and a' = acceleration)
Now
∴ The time period,
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An electric dipole of length 4 cm, when placed with its axis making an angle of 60° with a uniform electric field, experiences a torque of `4sqrt3`Nm. Calculate the potential energy of the dipole, if it has charge ±8 nC
Depict the equipotential surfaces due to an electric dipole.
(a) Define torque acting on a dipole of dipole moment \[\vec{p}\] placed in a uniform electric field \[\vec{E}\] Express it in the vector from and point out the direction along which it acts.
(c) What would happen if the external field
Write the expression for the torque \[\vec{\tau}\] acting on a dipole of dipole moment \[\vec{p}\] placed in an electric field \[\vec{E}\].
Find the resultant electric field due to an electric dipole of dipole moment, 2aq, (2a being the separation between the charges ±± q) at a point distant 'x' on its equator.
Define electric dipole moment. Is it a scalar or a vector? Derive the expression for the electric field of a dipole at a point on the equatorial plane of the dipole.
It is said that the separation between the two charges forming an electric dipole should be small. In comparison to what should this separation be small?
Two-point charges Q1 = 400 μC and Q2 = 100 μC are kept fixed, 60 cm apart in a vacuum. Find the intensity of the electric field at the midpoint of the line joining Q1 and Q2.
In an electric dipole, at which point is the electric potential zero ?
The electric field at a point on the equatorial plane at a distance r from the centre of a dipole having dipole moment `vec "p"` is given by, (r >> separation of two charges forming the dipole, `epsilon_0 - ` permittivity of free space) ____________.
Electric field on the axis of a small electric dipole at a distance r is E1 and at a distance of 2r on its perpendicular bisector, the electric field is E2. Then the ratio E2: E1 is ______.
A conic surface is placed in a uniform electric field E as shown in the figure such that the field is perpendicular to the surface on the side AB. The base of the cone is of radius R, and the height of the cone is h. The angle of the cone is θ.
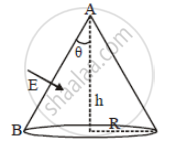
Find the magnitude of the flux that enters the cone's curved surface from the left side. Do not count the outgoing flux (θ < 45°)
The ratio of the weight of a man in a stationary lift and in a lift accelerating downwards with a uniform acceleration α is 3 : 2. The acceleration of the lift is:
The electric intensity due to a dipole of length 10 cm and having a charge of 500 µC, at a point on the axis at a distance 20 cm from one of the charges in air, is:
In a non-uniform electric field, electric dipole experiences:-
The region surrounding a stationary electric dipole has ______
Electric dipole consists of two charges of magnitude 0.1 µC separated by a distance of 2 cm. The dipole is in 5 an external field of 105 N/C. What maximum torque does the field exert on the dipole?
A dipole is placed in an electric field as shown. In which direction will it move?